January 15, 2025
4 min learn
Wildfires Began by Each day Human Actions Are Typically Extra Damaging
Quick-moving fires, such because the current ones within the Los Angeles space, and people began by people, whether or not by accident or not, are sometimes a few of the most harmful
Fireplace engines drive via flames ripping throughout Freeway 36 because the Park hearth continues to burn close to Paynes Creek in unincorporated Tehama County, California on July 26, 2024.
Josh Edelson/AFP through Getty Photos
The next essay is reprinted with permission from ![]() The Dialog, a web based publication protecting the newest analysis.
The Dialog, a web based publication protecting the newest analysis.
Investigators are attempting to find out what brought about a number of wind-driven wildfires which have destroyed 1000’s of properties throughout the Los Angeles space in January 2025. Given the fires’ places, and lack of lightning on the time, it’s doubtless that utility infrastructure, different gear or human actions had been concerned.
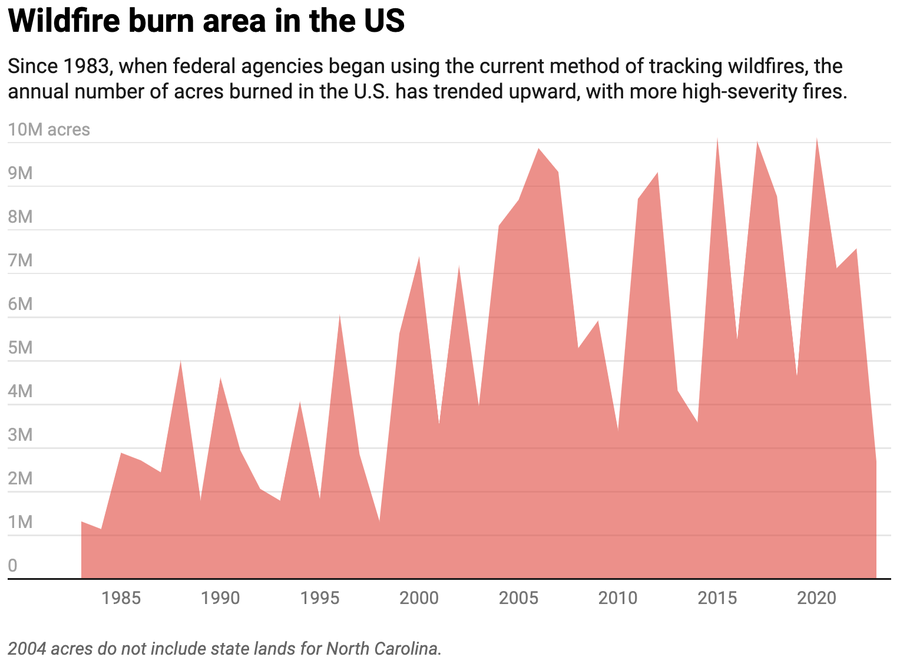
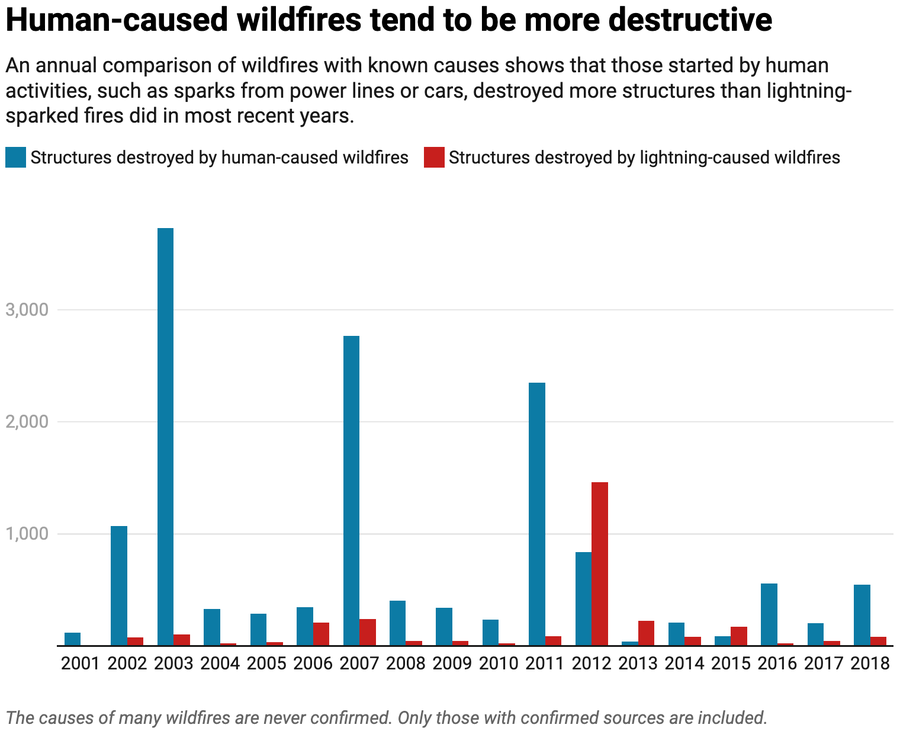
California’s wildfires have grow to be more and more harmful in recent times. Analysis my colleagues and I’ve carried out exhibits U.S. wildfires are as much as 4 instances bigger and 3 times extra frequent than they had been within the Nineteen Eighties and ’90s. Quick-moving fires have been significantly harmful, accounting for 78% of constructions destroyed and 61% of suppression prices between 2001 and 2020.
On supporting science journalism
In case you’re having fun with this text, contemplate supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world right now.
Lightning strikes are a typical explanation for U.S. wildfires, however the majority of wildfires that threaten communities are began by human actions.
A damaged energy line began the lethal 2023 Maui hearth that destroyed the city of Lahaina, Hawaii. Steel from vehicles or mowers dragging on the bottom can spark fires. California’s largest hearth in 2024 began when a person pushed a burning automobile right into a ravine close to Chico. The fireplace destroyed greater than 700 properties and buildings.
What makes these wildfires so harmful and troublesome to include?
The reply lies in a mixture of wind velocity, altering local weather, the legacy of previous land-management practices, and present human actions which can be reshaping hearth habits and rising the chance they pose.
Fireplace’s excellent storm
Wildfires depend on three key parts to unfold: conducive climate, dry gas and an ignition supply. Every of those components has undergone pronounced modifications in current a long time. Whereas local weather change units the stage for bigger and extra intense fires, people are actively fanning the flames.
Local weather and climate
Excessive temperatures play a harmful function in wildfires. Warmth dries out vegetation, making it extra flammable. Underneath these situations, wildfires ignite extra simply, unfold sooner and burn with better depth. Within the western U.S., aridity attributed to local weather change has doubled the quantity of forestland that has burned since 1984.
Compounding the issue is the speedy rise in nighttime temperatures, now rising sooner than daytime temperatures. Nights, which used to supply a reprieve with cooler situations and better humidity, achieve this much less typically, permitting fires to proceed raging with out pause.
Lastly, winds contribute to the speedy growth, elevated depth and erratic habits of wildfires. Wind gusts push warmth and embers forward of the hearth entrance and may trigger it to quickly develop. They’ll additionally create spot fires in new places. Moreover, winds improve combustion by supplying extra oxygen, which might make the hearth extra unpredictable and difficult to regulate. Normally pushed by excessive winds, fast-moving fires have grow to be extra frequent in current a long time.
Gas
Fireplace is a pure course of that has formed ecosystems for over 420 million years. Indigenous folks traditionally used managed burns to handle landscapes and scale back gas buildup. Nevertheless, a century of fireplace suppression has allowed huge areas to build up dense fuels, priming them for bigger and extra intense wildfires.
Invasive species, similar to sure grasses, have exacerbated the problem by creating steady gas beds that speed up hearth unfold, typically doubling or tripling hearth exercise.
Moreover, human improvement in fire-prone areas, particularly within the wildland-urban interface, the place neighborhoods intermingle with forest and grassland vegetation, has launched new, extremely flammable fuels. Buildings, autos and infrastructure typically ignite simply and burn hotter and sooner than pure vegetation. These modifications have considerably altered gas patterns, creating situations conducive to extra extreme and harder-to-control wildfires.
Ignition
Lightning can ignite wildfires, however people are chargeable for an rising share. From unattended campfires to arson or sparks from energy strains, over 84% of the wildfires affecting communities are human-ignited.
Human actions haven’t solely tripled the size of the hearth season, however in addition they have resulted in fires that pose a better threat to folks.
Lightning-started fires typically coincide with storms that carry rain or increased humidity, which slows fires’ unfold. Human-started fires, nevertheless, usually ignite underneath extra excessive situations– hotter temperatures, decrease humidity and stronger winds. This results in better flame heights, sooner unfold within the crucial early days earlier than crews can reply, and extra extreme ecosystem results, similar to killing extra timber and degrading the soil.
Human-ignited fires typically happen in or close to populated areas, the place flammable constructions and vegetation create much more hazardous situations. Properties and the supplies round them, similar to wood fences and porches, can burn rapidlyand ship burning embers airborne, additional spreading the flames.
As city improvement expands into wildlands, the likelihood of human-started fires and the property probably uncovered to fireplace improve, making a suggestions loop of escalating wildfire threat.
Whiplash climate
A phenomenon generally known as whiplash climate, marked by unusually moist winters and is derived adopted by excessive summer season warmth, was particularly pronounced in Southern California in recent times.
A moist spring in 2024 fostered vegetation progress, which then dried out underneath scorching summer season temperatures, turning into extremely flamable gas. This cycle fueled a few of the largest fires of the 2024 season, a number of of which had been began by people.
That dryness continued in Southern California via the autumn and into early winter, with little or no rainfall. Soil moisture within the Los Angeles area was about 2% of historic ranges for that point of 12 months when the fires started on Jan. 7, 2025.
Because the components that may drive wildfires converge, the potential for more and more extreme wildfires looms ever bigger. Extreme fires additionally launch giant quantities of carbon from timber, vegetation and soils into the environment, rising greenhouse fuel emissions and exacerbating local weather change, contributing to extra excessive hearth seasons.
This text was initially revealed on The Dialog. Learn the authentic article.

