A newly found galaxy has simply smashed the document for the earliest seen but, presenting a significant problem to our present fashions of galaxy formation.
It is known as JADES-GS-z14-0, and its brightly gleaming within the early Universe, because it regarded lower than 300 million years after the Huge Bang. A second latest discovery, known as JADES-GS-z14-1, was confirmed to be practically as distant.
The detections, astronomers say, at the moment are “unambiguous“, which implies the Cosmic Daybreak might need some ‘splainin’ to do.
“In January 2024, NIRSpec observed this galaxy, JADES-GS-z14-0, for almost ten hours, and when the spectrum was first processed, there was unambiguous evidence that the galaxy was indeed at a redshift of 14.32, shattering the previous most-distant galaxy record,” say astronomers Stefano Carniani of Scuola Normale Superiore in Italy and Kevin Hainline of the College of Arizona.
“From the images, the source is found to be over 1,600 light-years across, proving that the light we see is coming mostly from young stars and not from emission near a growing supermassive black hole. This much starlight implies that the galaxy is several hundreds of millions of times the mass of the Sun! This raises the question: How can nature make such a bright, massive, and large galaxy in less than 300 million years?”
Three separate papers have been uploaded to preprint server arXiv. They’re but to be peer-reviewed, however all three have the identical conclusion. JADES-GS-z14-0 is unquestionably there, a shining datapoint that represents a brand new approach ahead for understanding how the Universe fashioned, on the very starting.
Up till comparatively not too long ago, we had little or no concrete data concerning the interval often known as the Cosmic Daybreak, the primary billion or so years after the Huge Bang 13.8 billion years in the past. That is as a result of the early Universe was stuffed with a fog of impartial hydrogen that scattered gentle, stopping it from spreading.
This fog did not final; it was ionized and cleared by the ultraviolet gentle blazed out by objects within the early Universe, and by the tip of the Cosmic Daybreak, area was clear.
By then, nevertheless, there have been a complete bunch of stars and galaxies hanging round. If we wish to know the way it all fashioned, we’d like to have the ability to see into the fog.
This is without doubt one of the issues JWST, with its highly effective infrared eyes, was designed to do. Infrared radiation is ready to journey by way of dense media different gentle can’t, its lengthy wavelengths capable of move by way of with minimal scattering. It has been conducting the JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey (JADES), on the lookout for objects within the first 650 million years after the Huge Bang, with very attention-grabbing outcomes.
One factor that we have been repeatedly discovering is giant objects a lot sooner than we anticipate them. That is been fairly mind-blowing, as a result of we have been working below the belief that issues like supermassive black holes and galaxies take a very long time to kind – far longer than the timeframe through which we’re observing them.
However JADES-GS-z14-0 takes the cake. It is very giant, and really vibrant, under no circumstances what astronomers have predicted that galaxies appear to be within the early Universe. Firstly, the scale of it exhibits that a lot of the gentle must be coming from stars, reasonably than the blaze of sunshine from the area round a rising supermassive black gap.
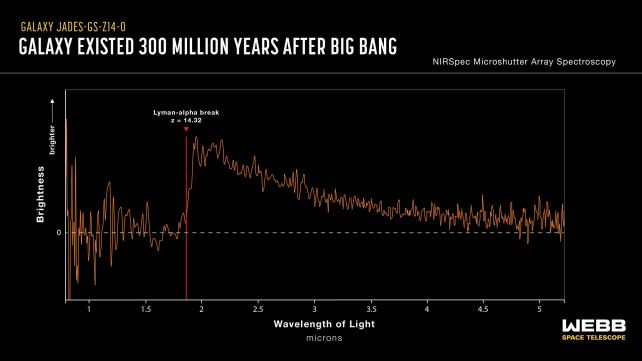
Evaluation of its gentle reveals the presence of a variety of mud and oxygen, which is sudden so early on. Such heavy components would should be made inside stars which then have to explode. These options recommend that a number of generations of huge stars will need to have lived and died already by 300 million years after the Huge Bang.
Provided that the very largest stars as we speak have lifespans of solely round a number of million years, that is not inconceivable, however nonetheless not fairly what astronomers anticipated to seek out.
All collectively, the galaxy means that we have to rethink the early Universe, displaying that the massive variety of gentle sources we see there can’t be solely defined by rising black holes. Someway, giant, vibrant, well-formed galaxies can assemble early within the Cosmic Daybreak.
“JADES-GS-z14-0 now becomes the archetype of this phenomenon,” Carniani says. “It is stunning that the Universe can make such a galaxy in only 300 million years.”
The invention paper led by Carniani might be discovered on arXiv. Simultaneous papers finding out the properties of the galaxy’s gentle might be discovered on arXiv right here and right here.

