November 27, 2024
4 min learn
What Makes the Jap U.S. Drought Totally different from the West’s
Drought is extra synonymous with the western U.S., however the japanese a part of the nation can descend into such circumstances surprisingly rapidly
The Manasquan Reservoir in New Jersey, which provides ingesting water to 1.2 million folks, dropped beneath half empty in mid-November.
Lokman Vural Elibol/Anadolu by way of Getty Photographs
Water ranges are dropping in reservoirs. A number of wildfires have ignited tinder-dry brush, exposing folks throughout the area to dangerous air air pollution ranges. It has barely rained for weeks.
This time we’re not speaking concerning the incessantly drought-plagued western U.S. however somewhat the usually wetter japanese portion of the nation—the place an unusually extreme drought has triggered water restrictions, broken crops and fed as many fires in six weeks as New Jersey usually sees in six months. A number of the results resemble these of dry durations out West, however drought within the East is a little bit of a unique beast.
The two halves of the nation have very completely different climates. A lot of the West has distinct moist and dry seasons: rain and blizzard from late autumn by early spring, and that’s largely it for the yr. Snow on the excessive western mountain peaks regularly melts throughout spring and summer season, protecting streams topped up and vegetation sufficiently watered when all goes nicely. However when winter precipitation is paltry or a scorching spring and summer season trigger fast snowmelt, there may be much less to maintain reservoirs crammed. Western states handle these sources to assist gird in opposition to a dry yr, however repeated years of failed rains and scorching climate can usher in disastrous drought. This occurred in California a decade in the past, when scorching climate formally pushed greater than half the state into “exceptional” drought standing—the very best class utilized by the U.S. Drought Monitor.
On supporting science journalism
If you happen to’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world as we speak.
A lot of the East Coast, however, can—and often does—see precipitation each month of the yr. Dry durations there “tend to be shorter-lived and not these same major disasters as in western North America,” says Benjamin Cook dinner, a local weather scientist at Columbia College’s Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, who research drought.
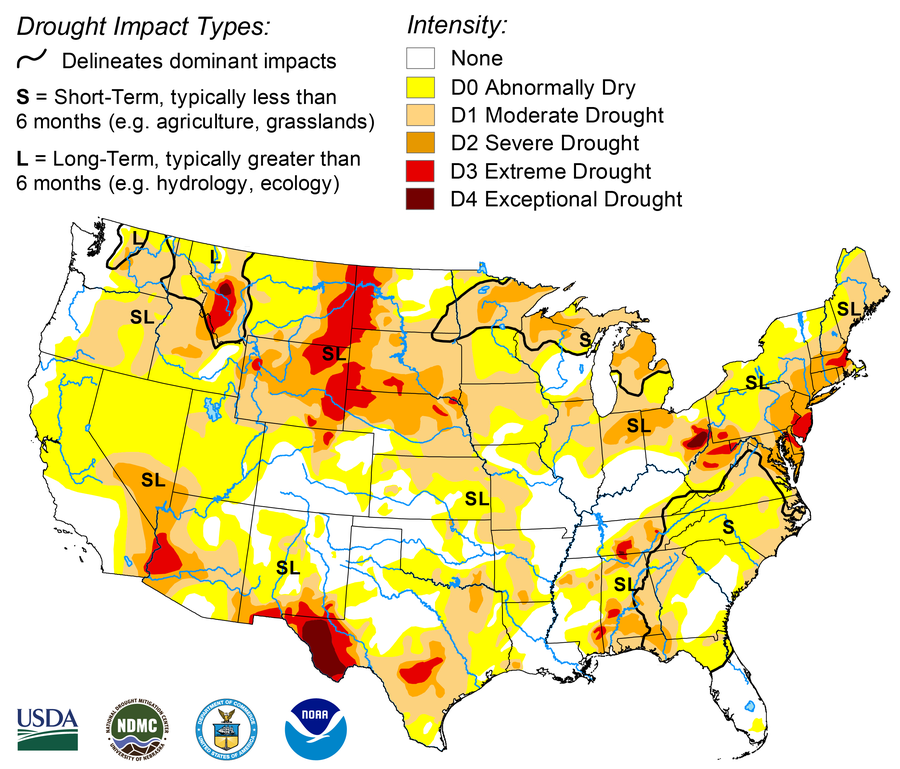
The U.S. Drought Monitor is collectively produced by the Nationwide Drought Mitigation Heart on the College of Nebraska-Lincoln, the US Division of Agriculture, and the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Map courtesy of NDMC.
However when a couple of weeks go by between rainstorms, drought can develop in a short time. This has significantly been the case this fall within the Northeast. After an especially moist winter and spring, many areas there noticed six weeks with little or no or no rain and unusually heat temperatures. And warmer temperatures improve evaporation, drying out the bottom and vegetation even quicker. “What’s wild is how far we’ve fallen down” by way of water within the Northeast, says David Boutt, a hydrologist on the College of Massachusetts Amherst. “All these lakes and streams are feet lower than they’re supposed to be.”
Wells are working dry in Connecticut. Officers in Philadelphia are intently monitoring the Delaware River’s “salt front”—the place its recent river water meets the salty water of the ocean—in case the ocean water pushes farther up the lowered river and threatens ingesting water provides. New York Metropolis has declared its first drought warning in 22 years, asking residents to take numerous steps to voluntarily reduce on water use. “It’s just not something that the Northeast typically deals with, so it’s shocking to read about,” says Denise Gutzmer, a drought influence specialist on the Nationwide Drought Mitigation Heart.
It might be worse. The drought of document in southern New England hit within the Sixties after years of below-normal rainfall. If those self same circumstances occurred now, with all of the inhabitants and infrastructure development since then, “we would be in really bad shape,” Boutt says. “Most places would be out of water or barely hanging on.”
The East Coast’s present dry circumstances have additionally made fall wildfires a lot worse than common; they’re igniting extra readily, and they’re burning hotter and longer. “We’re used to having some kind of reliable rain, and that helps put our fires out,” says Michael Gallagher, a U.S. Forest Service analysis ecologist, who research wildfires. This yr, although, “the fires keep popping up in more and more atypical places,” together with Prospect Park within the coronary heart of Brooklyn, N.Y., and small inexperienced areas in Manhattan.
One small factor that’s protecting the drought from being worse is that it’s taking place within the fall, when each folks and vegetation want much less water and there may be usually much less evaporation than within the warmth of summer season. However the seasonal timing can also be contributing to different wildfire-worsening components: for instance, deciduous bushes are dropping leaves, including extra potential gasoline for any spark.
A number of storms have introduced a small quantity of rain and snow to the area final week and this week, tamping down on fires and decreasing the chance of additional blazes. However they gained’t finish the drought; it can nonetheless take time for these rains so as to add as much as sufficient to erase the present deficit. “We’re not just one rainstorm away from everything being better again,” Gallagher says. Boutt concurs, saying, “The soils are just so dry” that it’s most likely going to take precipitation quantities of 10 inches, distributed over the subsequent few months, to get water ranges again as much as regular.
Precisely what the climate will carry for the remainder of the autumn and winter is unsure. Dependable climate forecasts solely lengthen about seven days into the longer term, and seasonal forecasts simply give the relative odds of what the climate over the subsequent few months will likely be. For the Northeast, the chances presently favor warmer-than-normal climate— however roughly equal probabilities of wetter or drier circumstances.
Wanting forward even additional, because the local weather continues to vary with rising temperatures, the work Boutt and others have accomplished means that vacillations between moist and dry durations within the Northeast are occurring extra incessantly, on the order of each two to 4 years.
For the remainder of this yr, the wildfire danger ought to not less than diminish a bit as the times get shorter and nights get colder. “It just doesn’t burn as well when it’s really cold out,” Gallagher says. That is significantly so when there may be an in a single day frost as a result of it takes time for that frost’s moisture to evaporate when the solar rises. Gallagher does warning, although, that main Northeast wildfires have occurred in each season. If a dry, windy climate sample takes maintain once more, hearth exercise might resume.
And even when there may be some rain and snow within the subsequent few months and hearth hazard stays low, there’s a specific amount of “memory’ in the water table, streams, rivers and lakes—it takes time for them to recover, Boutt says. “We’re going to be feeling this into spring and summer,” he provides.

