Within the yr 1181 CE, the sky exploded.
Effectively, part of the sky – a pinprick of nothing out of the blue blossoming into visibility, a brand new, momentary ‘visitor star’ within the constellation of Cassiopeia that astronomers in China and Japan watched and recorded for months.
That star was a supernova, the violent eruption as a useless white dwarf star accrued a lot mass from a binary companion that it exceeded crucial mass and blew its stack. It is considered one of vanishingly few such recorded occasions in human historical past, a vital laboratory for making an attempt to grasp the best way supernova remnants evolve over time.
Nonetheless, the fabric ejected by the white dwarf wasn’t to be found till 2013, increasing away from the positioning of the supernova in a spherical configuration, a supernova remnant named Pa 30. In 2023, astronomers found faint, skinny filaments contained in the sphere, like spokes connecting the ejecta to the white dwarf within the heart.
Now, these filaments have been mapped, and their velocity measured, with the Keck Cosmic Internet Imager (KCWI), giving us a brand new, three-dimensional map of the supernova remnants nonetheless blasting out into house, like the pinnacle of a dandelion gone to seed.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
“A typical picture of the supernova remnant can be like a static photograph of a fireworks show,” says physicist Christopher Martin of Caltech. “KCWI offers us one thing extra like a ‘film’ since we are able to measure the movement of the explosion’s embers as they streak outward from the central explosion.”
The supernova of 1181 CE, named SN 1181, is a rarity even amongst supernovae. In Kind Ia supernovae, a white dwarf slurps up an excessive amount of matter, exceeds the crucial mass restrict, and explodes with sufficient power to destroy the star. However there’s nonetheless a white dwarf on the heart of Pa 30.
The Kind Ia supernovae that go away behind a ‘zombie’ star are referred to as Kind Iax, and that is what we’re taking a look at with SN 1181. Astronomers consider that the occasion was not a typical mass switch to a white dwarf from a binary companion, however a merger between two white dwarfs, in order that’s fairly neat.
Led by astronomer Tim Cunningham of the Harvard & Smithsonian Middle for Astrophysics, a workforce of scientists used the KCWI instrument on the Keck Observatory in Hawaii to map the supernova remnant intimately. An correct map of what Pa 30 is doing now will help astronomers reconstruct what it was like previously.
The important thing to that is the best way gentle modifications when its supply is shifting. If a clump of matter is shifting in direction of us, the wavelength of the sunshine it emits is barely smooshed in direction of the shorter, bluer finish of the spectrum; and lightweight from an object shifting away is stretched in direction of the redder finish. Astronomers can research the quantity of smooshing and stretching and use it to determine how briskly one thing is shifting via house.
This allowed Cunningham and his workforce to calculate the pace of the SN 1181 ejecta. They decided that the fabric is increasing at a charge of about 1,000 kilometers (620 miles) per second. And that piece of the puzzle allowed them to rewind the explosion to when it happened.
“We find the material in the filaments is expanding ballistically,” says Cunningham. “This means that the material has not been slowed down nor sped up since the explosion. From the measured velocities, looking back in time, you can pinpoint the explosion to almost exactly the year 1181.”
That appears to clinch the connection between SN 1181 and Pa 30. However the analysis additionally revealed some new mysteries to unravel.
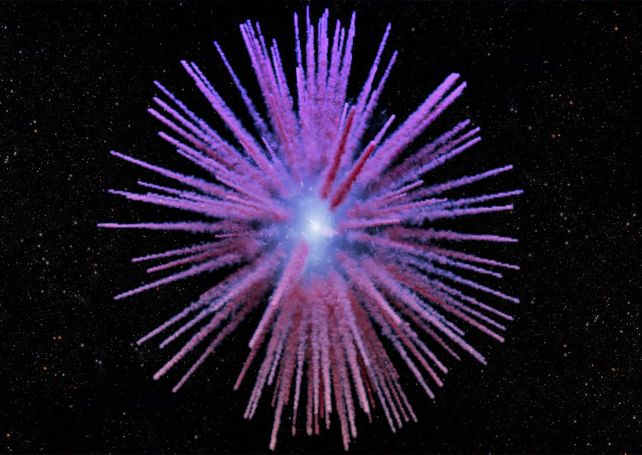
The research discovered proof of a powerful asymmetry in Pa 30 alongside our line of sight. This hints that the supernova explosion itself was asymmetrical. And there is a massive cavity within the heart of the remnant, across the zombie star within the heart. It is also unclear how the filaments themselves fashioned, after the explosion happened.
“A reverse shock wave may be condensing surrounding dust into filaments, but we don’t know yet,” says Cunningham. “The morphology of this object is very strange and fascinating.”
The research has been printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.

