On an unusual morning way back, on the foothills of what at the moment are the Pyrenees of Spain’s Iberian Peninsula, a bunch of Neanderthals woke, greeted the day, and set about their duties within the rising mild.
They might not have recognized that, tens of hundreds of years later, fashionable people scurrying about within the filth would discover traces of their existence, and be capable to reconstruct particulars about how they lived their lives. That, nonetheless, is precisely what archaeologists have now carried out – discovering that Neanderthals had been way more resilient than we suspected.
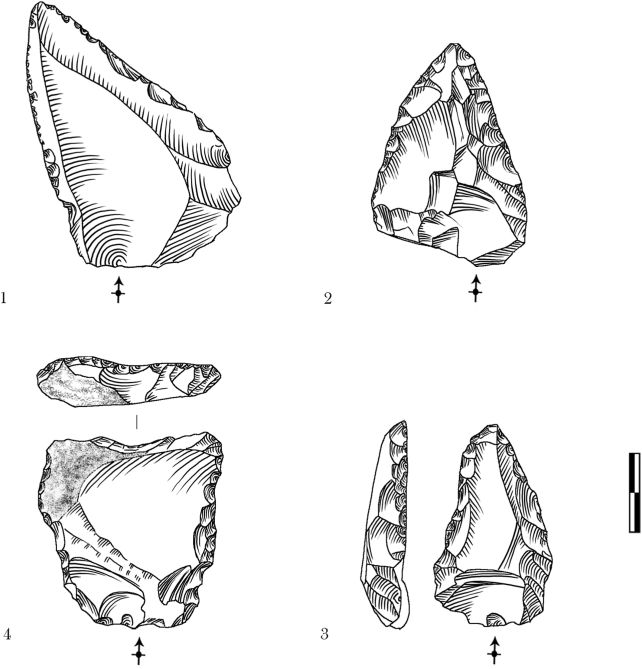
The excavation of a lately found rock shelter website referred to as Abric Pizarro has turned up hundreds of artifacts dated to between 65,000 and 100,000 years in the past, together with stone instruments and animal bones that may inform us rather a lot concerning the Neanderthal lifestyle throughout a interval for which few remnants stay.
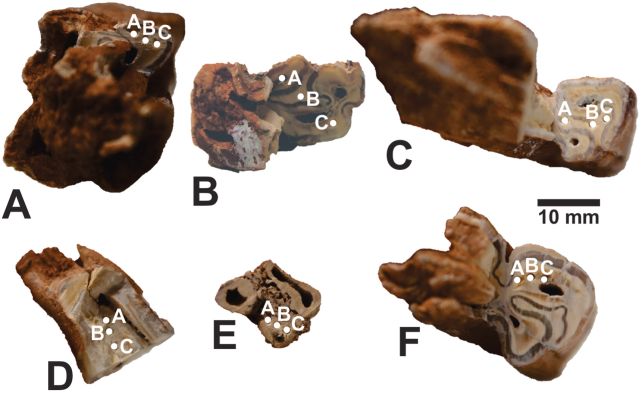
And, surprisingly, these bones embrace the stays of many small animals – revealing that Neanderthals had been versatile hunters, capable of adapt their way of life to meals availability.
“Our surprising findings at Abric Pizarro show how adaptable Neanderthals were,” says zooarchaeologist Sofia Samper Carro of the Australian Nationwide College.
“The animal bones we have recovered indicate that they were successfully exploiting the surrounding fauna, hunting red deer, horses and bison, but also eating freshwater turtles and rabbits, which imply a degree of planning rarely considered for Neanderthals.”
Neanderthals (Homo neanderthalensis) constituted one of many closest hominid family to fashionable people (Homo sapiens), to the purpose that the 2 species repeatedly mated, and might not even be a separate species in any respect. However for some cause, there was a persistent notion that Neanderthals had been primitive, uncultured, and cognitively much less developed than immediately’s people.
Lately, an increasing number of discoveries have been contradicting this notion. Neanderthals made subtle instruments, and embellished their setting with totally different sorts of artwork.
The principle downside with decoding the lives of the Neanderthals is the survivability of the artifacts they left behind. Neanderthals went extinct some 40,000 years in the past, and many of the detritus of their lives has succumbed to the ravages of time, decay, and erosion. What we’ve got been capable of recuperate means that the Neanderthals had been hunters solely of enormous prey, similar to horses and rhinoceroses.
Abric Pizarro was a Neanderthal rock shelter found in 2008, and archaeologists have been rigorously working to dig up its secrets and techniques since 2009. Samper Carro and her colleagues have now carried out an intensive survey of among the artifacts recovered.
The researchers carried out optically stimulated luminescence relationship to find out the age of the sediment during which the objects had been buried; that is a way that may decide when a mineral pattern was final uncovered to daylight.
Additionally they analyzed pollen grains and bones discovered on the website, wanting on the latter for indicators of lower marks and gnawing. And so they studied the stone instruments, to gauge the knapping methods and applied sciences accessible to the individuals who as soon as inhabited Abric Pizarro.
The relationship confidently confirmed the location was inhabited by Neanderthals roughly 70,000 years in the past, and the artifacts confirmed that these Neanderthals had been expert.
“The bones on this site are very well preserved, and we can see marks of how Neanderthals processed and butchered these animals. Our analysis of the stone artifacts also demonstrates variability in the type of tools produced, indicating Neanderthals’ capability to exploit the available resources in the area,” Samper Carro says.
“They clearly knew what they were doing. They knew the area and how to survive for a long time.”
This could not come as a lot of a shock. Neanderthals had been dwelling fortunately in Europe for round 300,000 years earlier than their extinction.
However the the reason why Neanderthals went extinct usually are not completely clear to us. If they’d been rigid of their strategy to meals availability, that may have been a clue. The truth that they had been adaptable can even inform us one thing about why they died out.
The speedy decline of the Neanderthals after surviving for therefore lengthy coincided with the arrival of contemporary people, a juxtaposition that doesn’t bode effectively for the function of our personal species of their disappearance. It might very effectively be the work of Homo sapiens that every one we’ve got left of the Neanderthals is a scant artifact report, and traces of DNA in our genome.
Now, we even have Abric Pizarro, and researchers are eager to sift out its secrets and techniques, to study extra concerning the mysterious lives of those long-lost cousins.
“Future studies will characterize the Neanderthal occupations documented in Abric Pizarro in more detail,” the authors write.
The analysis has been printed within the Journal of Archaeological Science.

