A severe knock to the top may additionally ship an insidious blow to the human immune system – a one-two punch that would reawaken dormant viruses within the physique, probably contributing to neurodegenerative illness.
A research utilizing stem cell ‘mini brains‘ has proven {that a} herpes simplex virus 1 (HSV-1) an infection already ‘arrested’ by the immune system can shake off its shackles when mind tissue is injured.
“We thought, what would happen if we subjected the brain tissue model to a physical disruption, something akin to a concussion?” says biomedical engineer Dana Cairns from Tufts College within the US.
“Would HSV-1 wake up and start the process of neurodegeneration?”
The reply appears to be sure. Whereas these mini brains aren’t excellent representations of an actual mind, they’re good fashions for the way mind tissue would possibly react when experiencing repeated, delicate blows to a ‘closed head’.
Per week after the damage, researchers seen the formation of clumps and tangles of proteins within the mind tissue, an indicator of neurodegenerative illnesses like Alzheimer’s.
A few of the mind cells additionally confirmed injury in keeping with neuroinflammation, and there have been important will increase in pro-inflammatory immune cells.
Traumatic mind accidents, together with continual traumatic encephalopathy (CTE), have lately emerged as a significant threat issue for neurodegenerative illnesses, and preliminary analysis suggests continual irritation from even delicate head trauma might play an element within the cumulative injury.
How that course of performs out isn’t but recognized, however different current research have discovered viruses might play a novel function. HSV-1 is a significant threat issue for neurodegeneration, presumably doubling the possibilities of growing dementia.
In a 2008 research, researchers found the genes of HSV-1 had been current in 90 % of the protein plaques in postmortem brains of Alzheimer’s sufferers. Nearly all of this viral DNA was discovered throughout the plaques.
To additional examine whether or not mind damage can reactivate an HSV-1 an infection, researchers at Tufts College and Oxford College turned to remoted mind slices. In response to bodily damage, these contaminated with latent HSV-1 secreted considerably much less of the excitatory neurotransmitter, glutamate.
Mini brains that had been aged for 8 weeks fared higher after damage than these aged for 4 weeks, indicating that head trauma might have extra profound results on younger growing brains.
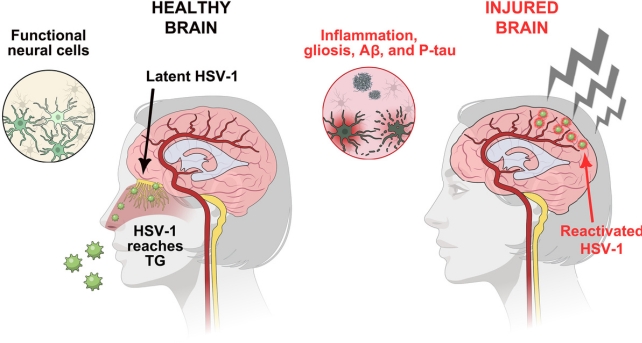
“Our results show that TBI causes reactivation of latent HSV-1 in our 3D brain model… and that if the injury is repeated, the damage is much greater than after a single blow,” the crew concludes.
Whether or not HSV-1 is awoken by bodily injury or one other pathogen, Cairns and her colleagues suspect this tremendous widespread virus is a contributing issue within the growth of dementia.
They argue future research ought to “investigate possible ways of mitigating or stopping the damage caused by head injury, such as anti-inflammatory and antiviral treatment after injury, thereby preventing HSV-1 reactivation in the brain and reducing subsequent development of Alzheimer’s disease.”
The research was revealed in Science Signaling.

