The open ocean can get fierce and wild.
There, whipped right into a frenzy, ocean swells and troughs can create partitions of water that dwarf our puny seafaring vessels, and wreak peril on the people courageous sufficient to enterprise asea.
Now, new experimental analysis reveals there’s rather more to those monstrous waves than we realized: they are often far bigger than we thought potential.
Our new understanding of the scale and complexity of ocean waves means that they are often as much as 4 instances greater than we knew. This lastly reveals how the so-called ‘rogue’ waves can attain the towering, harmful skyscraper heights recorded by means of historical past.
It is a discovery that actually piques the creativeness – but additionally has plenty of sensible functions, from climate and local weather modeling, to engineering and designing offshore constructions, in line with a crew led by engineer Mark McAllister of the College of Oxford.
“This is the first time we’ve been able to measure wave heights at such high spatial resolution over such a big area,” explains engineer Ross Calvert from the College of Edinburgh, “giving us a much more detailed understanding of complex wave breaking behavior.”
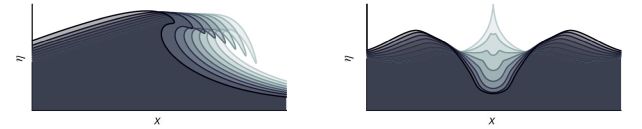
The specifics of wave formation and evolution are normally simplified to descriptions in simply two dimensions, transferring up and down, backwards and forwards. However the world is not flat, and as any surfer is aware of, waves within the ocean roll alongside a 3rd dimension as properly.
In the actual world, although, we are able to observe the best way waves behave. From this, we all know that touring waves achieve peak over distance, breaking once they attain most distance. That is when the white froth seems on the prime; as soon as that occurs, the wave curves in on itself and collapses.
That is the kind of wave we usually see on the seaside. However waves within the open ocean are completely different.
“The type of wave we studied occurs in open water and arises when waves coming from multiple directions come together,” says engineer Ton van den Bremer of the Delft College of Expertise within the Netherlands.
“When these waves with a high directional spread converge, the water is pushed upwards, forming a partially standing wave. An example of this is known as a crossing wave.”
So-called rogue waves are people who attain jaw-dropping heights, such because the well-known Draupner wave that reached 26 meters (85 toes), or a wave measuring a reported 42.7 meters within the Tasman Sea. These waves are the results of a number of waves touring in numerous instructions assembly at a central level.
This multidirectionality can occur the place two seas or currents meet, or when the winds all of the sudden change path. And the larger the distinction between the instructions of the waves – often called directional spreading – the taller the wave can develop into.
The researchers used a particular laboratory designed to check the habits of waves in the actual world, the FloWave Ocean Power Analysis Facility in Edinburgh. It consists of a round basin measuring 25 meters throughout – half the size of an Olympic pool – by which a number of waves may be generated in a number of instructions on the similar time.
It was in FloWave that the researchers replicated the Draupner wave, on which they revealed in 2019. Now, they’ve used information from the pool to check ocean waves in three dimensions, giving new perception into how these marine monsters emerge. And so they found one thing fascinating about rogue waves: their peak will not be restricted to the peak at which they break.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
“As soon as a traditional wave breaks, it kinds a white cap, and there’s no means again,” van den Bremer says. “However when a wave with a excessive directional spreading breaks, it will possibly continue to grow.”
Such waves, the researchers found, can develop to twice the peak that they have been at once they began breaking, which was already twice the peak at which typical waves break. This implies they are often 4 instances taller than the earlier theoretical restrict.
Offshore constructions reminiscent of generators are sometimes designed primarily based on a two-dimensional understanding of wave habits. Having a extra full image of their complexity will enable engineers to design extra sturdy constructions, capable of stand up to the buffeting to which they are going to be subjected by the wild sea.
The analysis has been revealed in Nature Communications.

