Researchers have suspected for a while that the hyperlink between our intestine and mind performs a task within the growth of Parkinson’s illness.
A current research recognized intestine microbes more likely to be concerned and linked them with decreased riboflavin ( vitamin B2) and biotin (vitamin B7), pointing the best way to an unexpectedly easy therapy that will assist: B nutritional vitamins.
“Supplementation of riboflavin and/or biotin is likely to be beneficial in a subset of Parkinson’s disease patients, in which gut dysbiosis plays pivotal roles,” Nagoya College medical researcher Hiroshi Nishiwaki and colleagues write of their paper revealed in Might.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
The neurodegenerative illness impacts nearly 10 million folks globally, who at finest can hope for therapies that gradual and alleviate signs.
Signs usually start with constipation and sleep issues, as much as 20 years earlier than progressing into dementia and the debilitating lack of muscle management.
Earlier analysis discovered folks with Parkinson’s illness additionally expertise adjustments of their microbiome lengthy earlier than different indicators seem.
Analyzing fecal samples from 94 sufferers with Parkinson’s illness and 73 comparatively wholesome controls in Japan, Nishiwaki and staff in contrast their outcomes with knowledge from China, Taiwan, Germany, and the US.
Whereas completely different teams of micro organism had been concerned within the completely different nations examined, all of them influenced pathways that synthesize B nutritional vitamins within the physique.
The researchers discovered the adjustments in intestine micro organism communities had been related to a lower in riboflavin and biotin in folks with Parkinson’s illness.
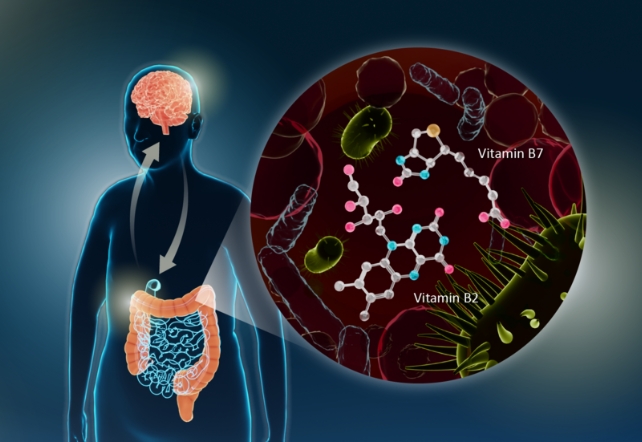
Nishiwaki and colleagues then confirmed the shortage of B nutritional vitamins was linked to a lower in short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and polyamines: molecules that assist create a wholesome mucus layer within the intestines.
“Deficiencies in polyamines and SCFAs could lead to thinning of the intestinal mucus layer, increasing intestinal permeability, both of which have been observed in Parkinson’s disease,” Nishiwaki explains.
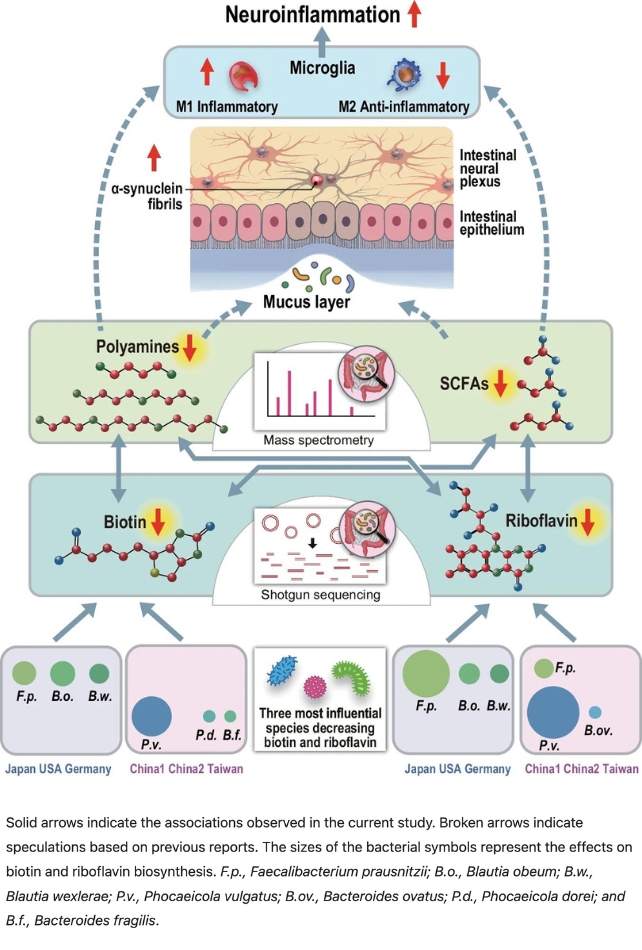
They believe the weakened protecting layer exposes the intestinal nervous system to extra of the toxins we now encounter extra usually. These embrace cleansing chemical substances, pesticides, and herbicides.
Such toxins result in the overproduction of α-synuclein fibrils – molecules recognized to amass in dopamine-producing cells within the substantia nigra a part of our brains, and elevated nervous system irritation, finally resulting in the extra debilitating motor and dementia signs of Parkinson’s.
A 2003 research discovered excessive doses of riboflavin can help in recovering some motor features in sufferers who additionally eradicated crimson meat from their diets.
So it is attainable that prime doses of vitamin B might stop a number of the injury, Nishiwaki and staff suggest.
This all suggests guaranteeing sufferers have wholesome intestine microbiomes can also show protecting, as would lowering the poisonous pollution in the environment.
After all, with such an advanced chain of occasions concerned in Parkinson’s illness, not all sufferers possible expertise the identical causes, so every particular person would should be assessed.
“We could perform gut microbiota analysis on patients or conduct fecal metabolite analysis,” explains Nishiwak.
“Using these findings, we could identify individuals with specific deficiencies and administer oral riboflavin and biotin supplements to those with decreased levels, potentially creating an effective treatment.”
This analysis was revealed in npj Parkinson’s Illness.
An earlier model of this text was revealed in June 2024.

