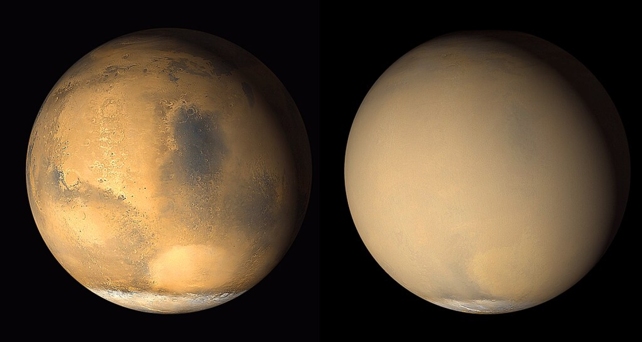
Mars is well-known for its mud storms, which happen each Martian 12 months throughout summer season within the southern hemisphere. Each three Martian years (5 and a half Earth years), these storms develop so massive that they’re seen from Earth and can engulf the complete planet for months.
These storms pose a major menace to robotic missions, producing electrostatic costs that may intrude with their electronics or trigger mud to construct up on their photo voltaic panels, stopping them from drawing sufficient energy to stay operational.
Whereas scientists have studied these storms for many years, the exact mechanisms that set off them have remained the topic of debate. In a new research, a workforce of planetary scientists on the College of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) has offered new perception into the elements concerned.
In keeping with their findings, comparatively heat and sunny days could kick off the most important storms each few years. These could possibly be step one towards forecasting excessive climate on Mars, which is significant for future crewed missions to Mars.
The research was led by Heshani Pieris, a graduate scholar on the Laboratory for Atmospheric and Area Physics (LASP) at CU Boulder. She was joined by Paul Hayne, a researcher at LASP and an affiliate professor on the Division of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences at CU Boulder.
Their findings have been introduced on the 2024 assembly of the American Geophysical Union, which passed off from December ninth to thirteenth in Washington, D.C.
Mars experiences mud storms recurrently, which regularly start as smaller storms that kind across the polar areas, normally throughout the second half of the Martian 12 months. These storms can develop quickly as they transfer in the direction of the equator till they cowl tens of millions of sq. kilometers.
Whereas these mud storms aren’t very highly effective resulting from Mars’ skinny ambiance (roughly 0.5% as dense as Earth’s), they will nonetheless pose a major hazard. Actually, world mud storms have been chargeable for the lack of the Alternative rover in 2018 and the InSight lander final 12 months.
“Dust storms have a significant effect on rovers and landers on Mars, not to mention what will happen during future crewed missions to Mars. This dust is very light and sticks to everything,” mentioned Pieris in a current press launch.
“Even though the wind pressure may not be enough to knock over equipment, these dust grains can build up a lot of speed and pelt astronauts and their equipment,” added Hayne. “We need to understand what causes some of the smaller or regional storms to grow into global-scale storms. We don’t even fully understand the basic physics of how dust storms start at the surface.”
For his or her research, Pieris and Hayne targeted on “A” and “C” storms, two climate patterns that are inclined to happen yearly on Mars. This consisted of analyzing knowledge gathered by the Mars Local weather Sounder instrument aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) over the course of 15 years (eight Mars years).
Particularly, they looked for durations of surprising heat, when extra daylight filtered by way of Mars’ skinny ambiance to warmth the planet’s floor. They found that roughly 68% of main storms on the planet have been preceded by a pointy rise in temperatures on the floor, which led to mud being kicked up.
Whereas these outcomes do not definitively show that hotter situations trigger mud storms, they point out that the identical phenomena that set off storms on Earth could also be at work on Mars. Throughout scorching summers in dry areas, heat air close to the floor can rise by way of the ambiance, resulting in massive grey clouds that sign rain.
Stated Pieris:
“When you heat up the surface, the layer of atmosphere right above it becomes buoyant, and it can rise, taking dust with it. This study is not the end all be all of predicting storms on Mars. But we hope it’s a step in the right direction.”
Pieris and Hayne are actually gathering more moderen observations of Mars to proceed investigating these explosive climate patterns. Ultimately, they hope that scientists will be capable to predict climate patterns on Mars based mostly on reside knowledge from the planet.
This text was initially revealed by Universe Right this moment. Learn the authentic article.

