Homeostasis is the upkeep of a comparatively secure inner atmosphere inside an organism, regardless of adjustments in exterior circumstances. It’s a essential course of for the right functioning of cells, tissues, and organs within the physique, making certain that important variables like temperature, pH, blood strain, and glucose ranges stay inside optimum ranges. The physique makes use of each the nervous and endocrine techniques to control homeostasis, with every system enjoying a selected function within the total course of. Amongst these, the central nervous system (CNS) is a key participant in coordinating and regulating lots of the important processes that contribute to homeostasis.
The Function of the Nervous System and Endocrine System in Homeostasis
The nervous system and the endocrine system are the first techniques liable for sustaining homeostasis. Each techniques regulate a variety of physiological processes, however they achieve this in numerous methods:
- Endocrine System: The endocrine system features by secreting hormones into the bloodstream, which then journey to focus on cells and organs. These hormones regulate a wide range of features comparable to progress, metabolism, and reproductive processes. Nonetheless, the results of the endocrine system are usually slower, usually taking hours or days to manifest.
- Nervous System: In distinction, the nervous system makes use of electrical indicators within the type of motion potentials to transmit data quickly throughout the physique. These motion potentials excite or inhibit goal cells, permitting for fast responses to inner and exterior adjustments. This makes the nervous system a right away and extremely responsive regulator of homeostasis.
Key Constructions within the CNS Concerned in Homeostasis
Two essential constructions within the CNS are immediately liable for sustaining homeostasis: the reticular formation and the hypothalamus.
Reticular Formation: Regulating Important Capabilities
The reticular formation is a fancy community of neurons positioned within the brainstem, which performs an important function in regulating a wide range of physiological processes which are essential for sustaining homeostasis. It controls features of many inner organs, comparable to the guts, lungs, and digestive system, in addition to influencing facets of habits.
Inside the reticular formation, a number of facilities assist regulate homeostasis:
- Vasopressor Heart: This middle will increase the speed and pressure of cardiac contractions, inflicting the blood vessels to constrict (vasoconstriction). These actions end in a rise in blood strain, which ensures sufficient blood movement to organs and tissues.
- Vasodepressor Heart: Conversely, the vasodepressor middle decreases the speed and pressure of coronary heart contractions, whereas inflicting blood vessels to dilate (vasodilation). This results in a lower in blood strain, serving to to stop hypertension and promote wholesome circulation.
Moreover, the reticular formation accommodates nuclei that assist management digestive processes and urination, each of that are essential for sustaining fluid and nutrient stability within the physique.
Hypothalamus: The Grasp Regulator of Homeostasis
The hypothalamus, a small however highly effective area of the mind, is maybe a very powerful construction in regulating homeostasis. It’s anatomically and functionally linked to the pituitary gland, reflecting the shut relationship between the nervous and endocrine techniques. The hypothalamus is liable for sustaining stability in numerous important features, together with physique temperature, starvation, thirst, and sleep.
Hypothalamus and Temperature Regulation
One of many key roles of the hypothalamus is to control physique temperature. It acts because the physique’s thermostat by establishing a set level of roughly 37°C (98.6°F) as the conventional temperature. The hypothalamus receives enter from temperature-sensitive neurons positioned within the pores and skin, deep tissues, and throughout the hypothalamus itself. If the physique turns into too sizzling or too chilly, the hypothalamus prompts mechanisms to carry the temperature again to the set level:
- If the physique is simply too heat, the hypothalamus triggers cooling mechanisms, comparable to sweating and vasodilation (enlargement of blood vessels), to dissipate warmth.
- If the physique is simply too chilly, the hypothalamus induces warming responses, comparable to shivering and vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), to preserve warmth.
Hypothalamus and Feeding Regulation
The hypothalamus additionally performs a essential function in regulating feeding habits. It helps keep vitality stability by monitoring blood glucose ranges and the storage of fat. Stimulation of sure hypothalamic nuclei induces starvation, prompting the person to hunt meals. This regulatory mechanism not directly helps keep homeostasis by making certain glucose ranges stay secure. The hypothalamus additionally indicators satiety, stopping overeating and sustaining metabolic stability.
The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Controlling Inner Organs
A good portion of homeostasis is maintained by the autonomic nervous system (ANS), which controls the perform of the physique’s inner organs and constructions (viscera). The ANS regulates important features comparable to coronary heart fee, blood strain, digestion, and urination—all of that are essential for sustaining homeostasis.
Whereas the ANS is technically a part of the peripheral nervous system (PNS), its features are primarily managed by the CNS, particularly the hypothalamus. The hypothalamus sends directions to the reticular formation within the brainstem, which then directs the autonomic facilities that regulate organ features. For instance:
- Coronary heart Fee and Blood Stress: The hypothalamus can improve or lower the speed and pressure of coronary heart contractions by the vasopressor and vasodepressor facilities within the reticular formation.
- Digestion and Urination: The hypothalamus influences the digestive system by regulating the secretion of digestive enzymes and gastric motility. It additionally controls the timing of urination by coordinating the autonomic pathways that affect the bladder.
The Function of Sleep in Homeostasis
Sleep is one other important course of regulated by the CNS. It’s thought of some of the elementary homeostatic processes, permitting the physique and mind to restore, rejuvenate, and consolidate reminiscences. Sleep follows a circadian rhythm, which is managed by the hypothalamus and is synchronized with the day-night cycle.
Circadian Rhythms and the Organic Clock
The hypothalamus accommodates a specialised area generally known as the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN), which features because the physique’s inner clock. The SCN is delicate to mild and darkness and helps coordinate the sleep-wake cycle. Throughout the evening, the SCN promotes sleep, whereas throughout the day, it triggers wakefulness.
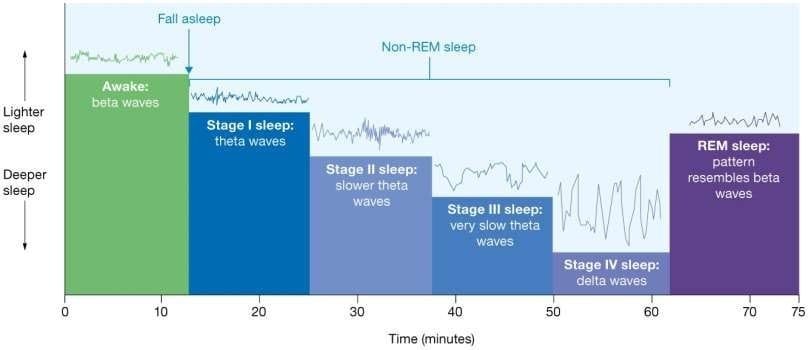
Mind Waves and Phases of Sleep
As we sleep, our mind strikes by totally different levels, every characterised by distinct patterns of mind wave exercise, which may be measured utilizing an electroencephalogram (EEG). These levels are categorised into non-REM (Fast Eye Motion) sleep and REM sleep:
- Beta Waves: These happen after we are awake and engaged in psychological exercise. They’re high-frequency, low-amplitude waves.
- Non-REM Sleep (Phases I-IV): These levels progress from mild drowsiness (Stage I) to deep sleep (Stage IV). As we transfer by levels I-III, mind waves gradual from beta waves to theta waves. Stage IV is marked by delta waves, representing deep, restorative sleep.
- REM Sleep: After Stage IV, we enter REM sleep, which is related to speedy eye actions and vivid dreaming. Mind wave patterns throughout REM sleep resemble these seen throughout wakefulness (beta waves), and this stage performs an important function in reminiscence consolidation and emotional processing.
The Significance of Sleep for Homeostasis
Sleep serves a number of features in sustaining homeostasis, together with bodily restoration, reminiscence consolidation, and emotional regulation. Throughout sleep, the physique repairs tissues, strengthens the immune system, and restores vitality ranges. Moreover, sleep performs a task in balancing hormones, comparable to progress hormone and cortisol, which affect metabolism, stress responses, and immune perform. Disruptions in sleep can have important penalties on homeostasis, resulting in points comparable to impaired cognitive perform, weakened immune response, and metabolic imbalances.
Conclusion: The CNS and Homeostasis
The central nervous system performs an important function in sustaining homeostasis by regulating essential bodily features by constructions such because the reticular formation and hypothalamus. These constructions work collectively to control processes like coronary heart fee, blood strain, digestion, temperature, feeding, and sleep. The CNS’s capability to coordinate these features ensures that the inner atmosphere stays secure, permitting the physique to adapt to each inner and exterior adjustments. By sustaining homeostasis, the CNS performs a elementary function in selling total well being and well-being. Understanding the intricate relationship between the CNS and homeostasis highlights the significance of sustaining a balanced way of life to help the optimum functioning of the nervous system.

