The embryos of many fish species have some management over after they hatch, successfully selecting their very own birthdays.
A research by researchers from Hebrew College of Jerusalem in Israel now reveals the chemical and organic processes enabling this to occur, exhibiting how particular person embryos time their emergence with optimum environmental components.
The scientists studied zebrafish (Danio rerio) eggs, discovering that the discharge of the thyrotropin-releasing hormone (Trh) from the embryo was essential in producing enzymes to dissolve the egg wall.
“Hatching is a crucial occasion within the life historical past of oviparous species,” the researchers write of their revealed paper.
“The decision to hatch is often carefully timed to coincide with favorable conditions that will improve survival through early life stages.”
Fish species use many various hatching methods and triggers: zebrafish, for instance, often look ahead to daylight. Clownfish and halibut look ahead to darkness. California grunion wait to be washed out to sea.
The analysis presents proof of the mechanisms at work behind this delay. In zebrafish, TRH is delivered to the hatching gland through the bloodstream, on the instruction of a neural circuit that is fashioned simply earlier than hatching and disappears simply after.
And it isn’t simply zebrafish: the researchers additionally studied the medaka (Oryzias latipes), a distantly associated species.
The evolutionary pathways of medaka and zebrafish separated some 200 million years in the past, however the identical Trh-triggered hatching course of was recognized within the two species’, despite their variations in hatching glands, enzyme sorts, and embryonic intervals.
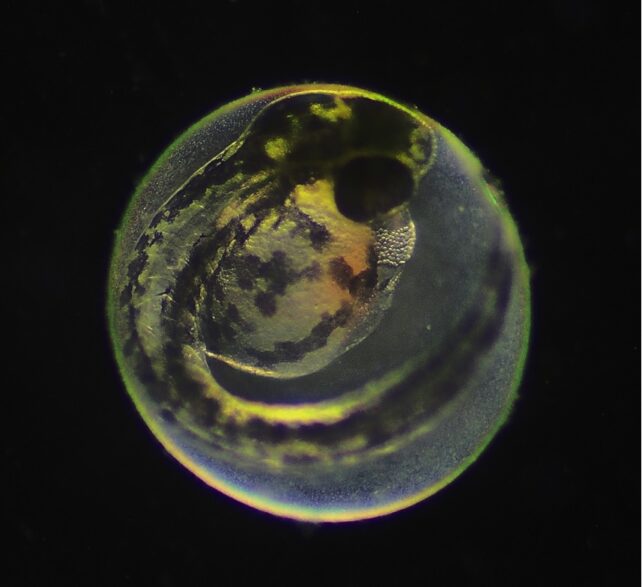
“Using immunostaining, we observed that like zebrafish, medaka embryos form a transient Trh circuit shortly before hatching that disappears in post-hatching
larvae,” write the researchers.
In people and different mammals, Trh helps management key organic processes, together with coronary heart fee and metabolic fee. It is notable that the identical neurohormone can be used otherwise in fish, maybe one other pointer to diverging evolutionary paths.
The researchers at the moment are eager to research particulars of the hatching course of in zebrafish, in addition to the similarities and variations there may be in different aquatic species with totally different approaches to hatching.
Local weather change is one other consideration for future analysis: because the world will get hotter, if we’re going to have the ability to protect species for generations to return, we have to perceive how larger temperatures would possibly affect hatching decision-making that has developed over a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of years.
“It would be interesting to test how conserved the role of Trh is in this process and study variation in the structure and function of the hatching circuitry between species with different hatching strategies,” write the researchers.
The analysis has been revealed in Science.

