The next essay is reprinted with permission from The Dialog, an internet publication protecting the newest analysis.
It took a worldwide pandemic to persuade American companies that their workers might work productively from house, or a favourite espresso store. Put up-COVID-19, employers are struggling to search out the suitable stability of in-office and distant work. Nonetheless, hybrid work is probably going right here to remain, no less than for a phase of employees.
This shift isn’t simply altering life – it’s additionally affecting industrial areas. Workplace emptiness charges post-COVID-19 shot up virtually in a single day, they usually stay close to 20% nationwide, the best fee since 1979 as tenants downsize in place or relocate. This workspace surplus is placing strain on current improvement loans and resulting in defaults or inventive refinancing in a market already suffering from larger rates of interest.
On supporting science journalism
In case you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world immediately.
Workplace tenants with deeper pockets have gravitated to newer and bigger buildings with extra facilities, sometimes called Class A or “trophy” buildings. Older Class B and C buildings, which regularly have fewer facilities or less-desirable areas, have struggled to fill house.
Excessive emptiness charges are forcing builders to get inventive. With diminished demand for older buildings, together with housing shortages in lots of American cities, some downtown buildings are being transformed to residential use.
These initiatives usually embody some share of reasonably priced housing, underwritten by tax incentives. In October 2023, the Biden administration launched a listing of federal mortgage, grant, tax credit score and technical help packages that may help commercial-to-residential conversions.
As an architect, I’m inspired to see these renovations of older industrial buildings, that are extra economical and sustainable than new development. In my opinion, they’re essentially altering the character of our cities for the higher. Although solely about 20% to 30% of older buildings will be profitably transformed, architects and builders are shortly studying learn how to grade these constructions to determine good candidates.
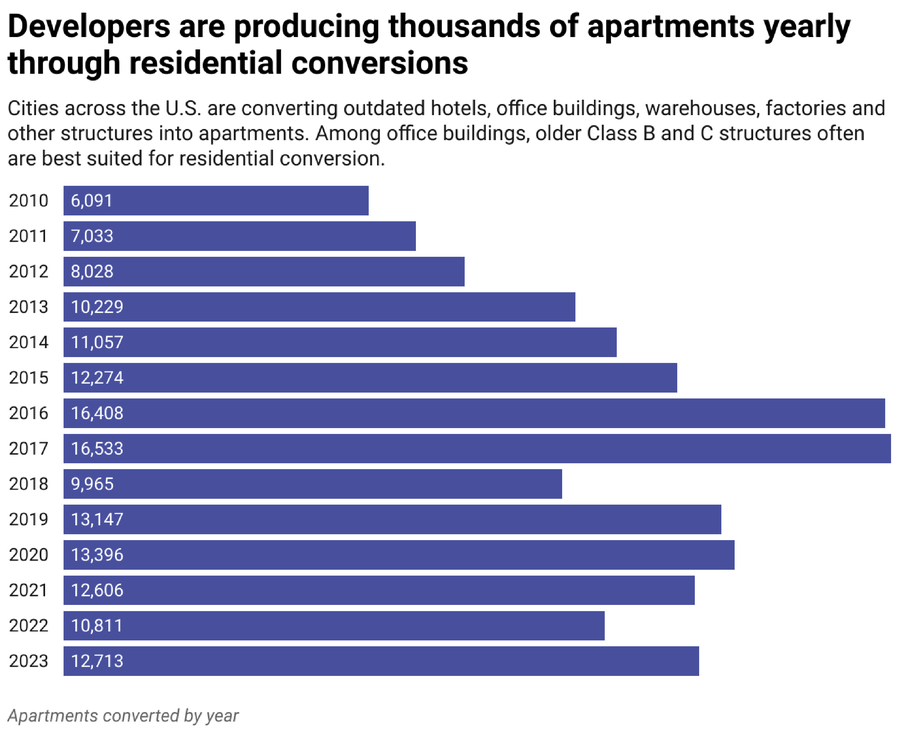
The Dialog (CC BY-ND); Supply: RentCafe
From office to residing house
Changing industrial buildings to flats didn’t begin with the pandemic. Within the decade main as much as the outbreak of COVID-19, builders transformed greater than 110,000 flats from outdated accommodations, workplace buildings, factories, warehouses and different buildings throughout the U.S. Based on business information, greater than 58,000 flats are at present being transformed from workplace buildings.
A number of traits of older Class B and C buildings make conversion notably enticing. These buildings usually have smaller flooring plates – whole sq. footage of house per flooring. Importantly, additionally they have shorter “core-to-shell” distances – the space from the constructing core that comprises stairs and elevators to the window wall.
Residential constructing codes typically require that pure gentle attain most rooms. Since residing areas, bedrooms and loos are sometimes separated by partitions, a smaller core-to-shell distance permits extra rooms to entry pure gentle, making the conversion simpler.
In distinction, typical new workplace buildings have bigger flooring plates and core-to-shell distances that generally can exceed 50 toes. This makes them tougher to transform to residences.
However it’s not inconceivable. One inventive resolution entails shifting the window wall inward by a number of toes to create outside decks. That’s an interesting amenity, but in addition an additional value. In some conversions the place the core-to-shell depth is bigger than wanted, builders have added inside vertical shafts or window wells to deliver daylight to inside areas.
Many older industrial buildings additionally provide larger ceilings, that are particularly fascinating within the residential market. Residences and condos usually don’t want to hide mechanical and electrical companies with suspended acoustic tile ceilings, as workplaces do, to allow them to present 12 toes or extra of clear ceiling peak.
Some older buildings, together with many product of brick or stone, have massive home windows, which are also fascinating in residential use. Conversely, smaller home windows or larger sill heights could also be disincentives to conversion.
Many older buildings have been constructed earlier than air-con was extensively obtainable, so that they have operable home windows. That is one more plus for residential conversion, since occupants usually want pure air flow of their dwelling unit.
Obstacles to conversion
Some traits of older buildings could make residential conversion tougher. For instance, location all the time issues. Buildings which can be removed from different facilities, corresponding to eating places or grocery shops, could also be much less fascinating.
Buildings with extra uncommon flooring plates or geometric types that work for workplace use could also be troublesome to carve up into residential models. Older constructions that comprise asbestos or lead paint can require costly remediation.
Zoning legal guidelines might bar residential use or in any other case restrict what will be completed with a constructing. Cities can play an essential function in encouraging residential conversions by revisiting zoning codes or providing tax incentives to builders.
One of many greatest prices of a residential conversion is the necessity to exchange constructing methods corresponding to plumbing and heating. Plumbing necessities in industrial workplace areas, for instance, are largely met with restroom services within the constructing core. Residences or condos every require their very own lavatory and kitchen, including vital value.
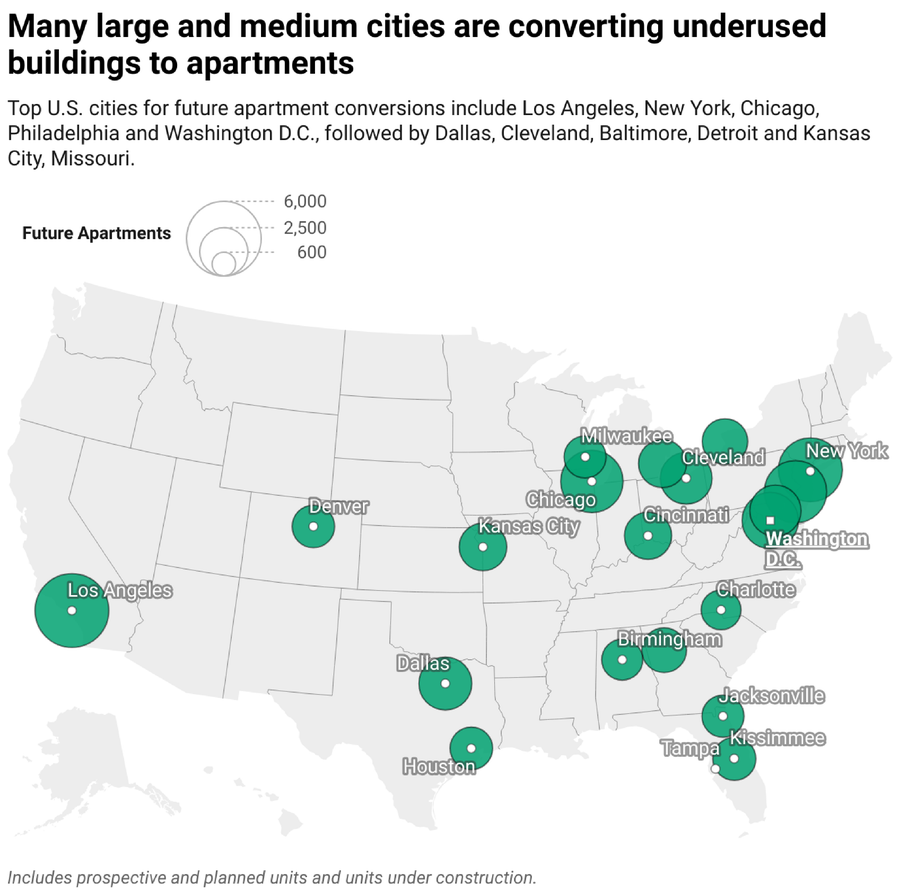
The Dialog (CC BY-ND); Supply: RentCafe
A return to ‘walkable cities’
Regardless of these challenges, if residential conversions deliver individuals and power again to downtowns exterior of the workday, shops, eating places, leisure and different facilities of a vibrant life-style will comply with.
Architects, planners, builders and politicians are more and more keen on “walkable cities” or “20-minute cities.” Each of those ideas allude to offering essential facilities like grocery shops, colleges and eating places which can be accessible to residents on foot, decreasing the necessity to personal a automotive and selling a extra sustainable life-style.
Walkable cities aren’t a brand new thought. All through the nineteenth century, individuals in U.S. cities like New York and Chicago lived, labored, shopped and socialized inside mixed-use neighborhoods.
The expansion of automotive possession post-World Struggle II separated these makes use of into residential suburbs, workplace parks, buying malls and cineplexes. Many critics view suburbanization as a failed experiment that has promoted sprawling improvement, reliance on automobiles and financial inequality
As extra downtown workplace buildings are transformed to residential use, a lot of them are more likely to home eating places, day care services, grocery shops and different service companies, usually on their floor flooring. These facilities contribute to the monetary success of a venture and to the colourful life of its residents.
All of those shifts immediate questions. Can architects and builders discover methods to design buildings that serve a number of makes use of over a number of centuries, slightly than a single focused use that turns into out of date in 100 years? Can mid- and high-rise buildings be envisioned as versatile structural grids, with lower-cost and simply changeable modular inserts? Such constructions might accommodate ever-changing wants, a few of which we might not but know can be essential to the city infrastructure.
Architects, planners and builders are starting to discover these questions. Changing downtown workplaces to residential use may very well be simply the place to begin. And it’s a reminder that dynamic cities can reinvent themselves in response to challenges.
This text was initially revealed on The Dialog. Learn the authentic article.

