January 23, 2025
5 min learn
Saturn’s Rings Are Disappearing—However They’ll Be Again
This yr, from Earth’s perspective, Saturn’s rings will seem almost edge on, making them virtually invisible
Saturn’s rings, imaged right here by NASA’s Cassini orbiter, are one of many photo voltaic system’s most reliably spectacular sights. However typically they appear to vanish as seen from Earth.
NASA/JPL/Area Science Institute
I just lately observed one thing odd about Saturn whereas admiring it close to good Venus within the southwestern night time sky. Any object near our evil twin sister planet will look considerably uninteresting compared—Venus could be so brilliant that it’s generally mistaken for an airplane or a UFO—however Saturn regarded positively glum. It’s virtually on the opposite aspect of the solar from us proper now, so it’s almost at its most distance from Earth and thus considerably fainter than common. However nonetheless, it simply appeared particularly dim.
Then I remembered: Saturn’s good rings are disappearing—not less than they’re from our perspective right here on Earth. The usually broad rings presently seem a lot slimmer than common, virtually like a line throughout the planet. With out their numerous reflective icy chunks including to our view of Saturn’s luster, the planet actually is lower than half as brilliant as it may be at different occasions.
Relaxation assured, Saturn’s magnificent rings are nonetheless there! There are two causes they’re nearly invisible: one is that they’re virtually unimaginably flat, and the opposite is that our viewing angle is affected by the dance of Saturn’s and Earth’s respective orbits.
On supporting science journalism
Should you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at the moment.
Saturn’s rings aren’t simply the obvious factor concerning the planet—they’re arguably essentially the most magnificent construction in your entire photo voltaic system. The primary rings are about 280,000 kilometers throughout; when you put them between Earth and the moon, they’d cowl greater than two thirds of that hole! At Saturn’s distance of greater than a billion kilometers from Earth, the rings, as giant as they’re, are invisible to the unaided eye—however solely simply barely: as quickly as we started scanning the sky with telescopes, the rings had been noticed, even when their true construction remained mysterious.
Galileo noticed the rings by means of his crude telescope within the early seventeenth century however didn’t have sufficient decision to see their true form, and he known as them Saturn’s “ears.” A long time later Dutch astronomer Christiaan Huygens realized that the planet was encircled by a hoop that was “touching it nowhere,” as he wrote within the e-book Systema Saturnium. A determine at least physicist James Clerk Maxwell—who decided the equations for electromagnetism that underpin our technological civilization—was the primary to show that such a hoop couldn’t be stable, or else it will get torn aside. The inside edge would revolve round Saturn a lot sooner than the periphery, shredding it. From this, it was discovered that the planet’s rings (plural) should be made up of chunks of fabric too small for any telescope from Earth to see. Extra trendy observations confirmed that these chunks are almost pure water ice—which is why they’re so brilliant; ice is a wonderful reflector of daylight. And trendy research additionally confirmed that the majority of those chunks are smaller than a median automobile. There should be quadrillions of them.
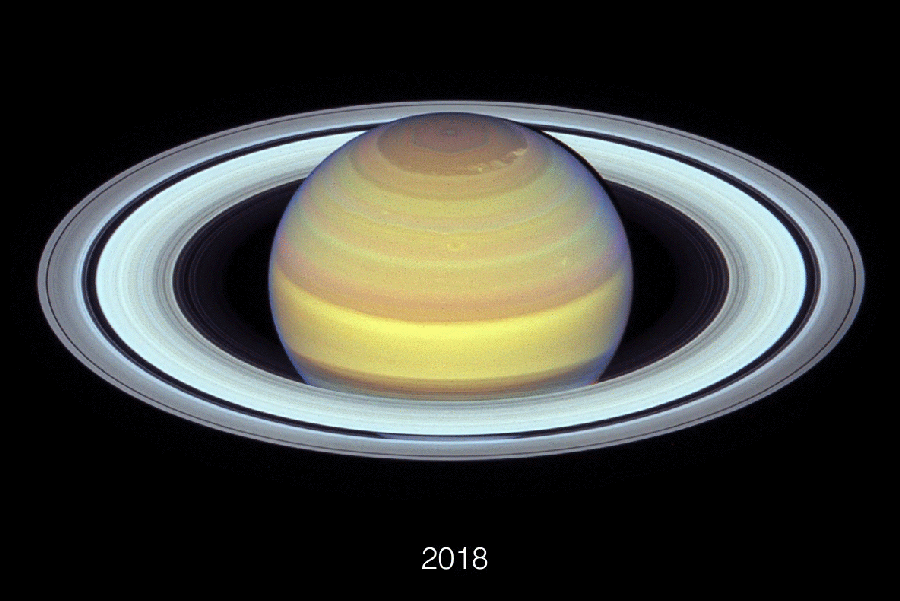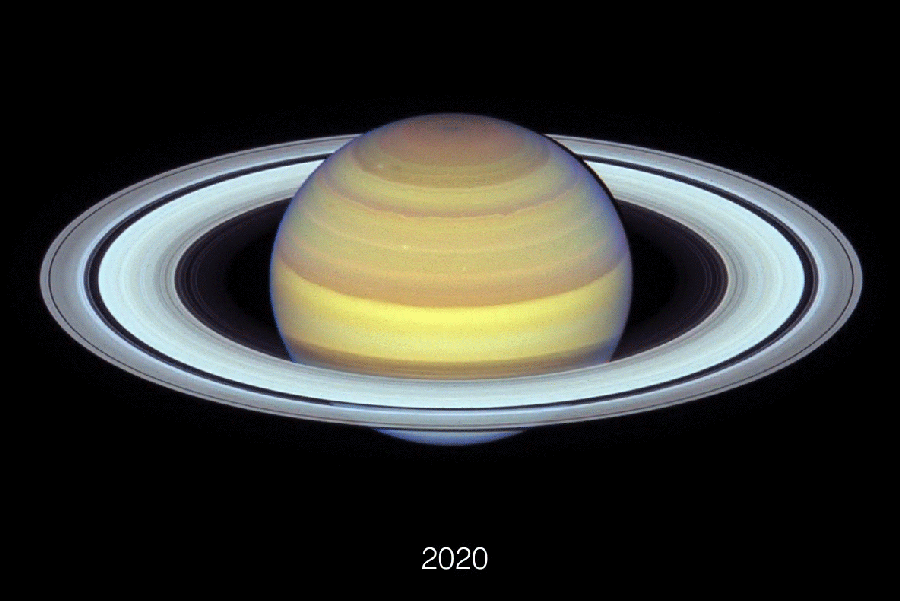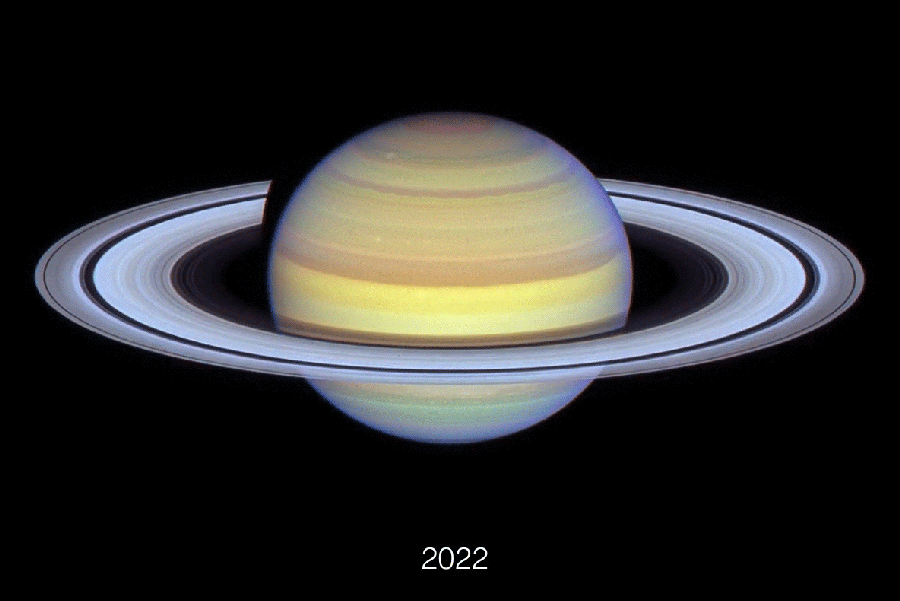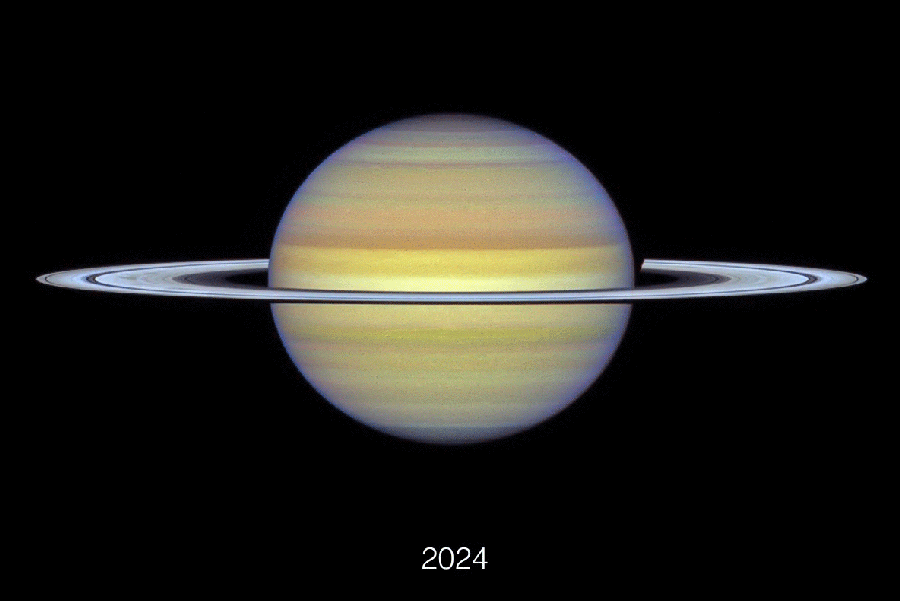
Composed of Hubble Area Telescope pictures, this animation exhibits Earth’s altering perspective on Saturn’s rings between 2018 and 2024.
NASA, ESA, Amy Simon (NASA-GSFC), Michael H. Wong (College of California), Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
The rings most likely shaped from an icy moon of Saturn getting whacked, laborious, by an incoming object, maybe even one other moon. Apparently, it’s not clear when this occurred. Analysis revealed within the journal Icarus in 2023 regarded on the accumulation charge of darkish micrometeorite mud on the in any other case shiny rings and located that the rings had been younger, cosmically talking: simply 100 million to 400 million years in age. Alternatively, analysis revealed in late 2024 within the journal Nature Geoscience discovered that the “pollution” charge from this mud isn’t as quick as had been thought; the high-speed micrometeorite collisions ionize the ring particles, giving them an electrical cost. That makes them prone to Saturn’s highly effective magnetic subject, which then attracts the fabric away, slowing the speed at which the rings darken. Meaning the rings could be far older.
Even at the moment, centuries after their discovery, the rings nonetheless pose elementary mysteries.
Nonetheless, how they shaped after the preliminary collision is comparatively effectively understood, and it explains their flatness, if not their age. Due to the orbital motions of the Saturnian moon and its impactor, the particles would possible have first shaped an extended stream, most of which might have lain within the route of that moon’s orbital movement. Saturn’s different moons orbit over its equator, so the fabric from this one would possible have wound up in an identical configuration as effectively. Additionally, as a result of Saturn isn’t an ideal sphere however as an alternative bulges on the equator from its speedy 10.5-hour rotation interval, the planet’s thickened center would have torqued particles into an orbit instantly over the equator; this is the reason a ring-generating affect would have shaped a flat disk.
And I do imply flat. Regardless of being lots of of hundreds of kilometers throughout, the rings are extraordinarily skinny, vertically spanning a kilometer at most. In some locations the rings are simply 10 meters excessive, as tall as a three-story constructing. As immense because the rings are, in the event that they and Saturn itself had been scaled down to twenty-eight centimeters (11 inches) throughout, the size of a typical sheet of paper, the rings could be 100 occasions as skinny because the paper! Lastly, gravitational interactions with Saturn’s giant moons pull these ring particles into barely completely different orbits. Over time, they’ve created hundreds of particular person rings, in addition to a handful of gaps amongst them. So from above, the rings are a supply of slack-jawed awe. From the aspect, although, they’re razor-thin and intensely tough to see.
That’s the place we discover ourselves now. Saturn, like Earth, has a big axial tilt that’s greater than 26 levels askew from the ecliptic airplane during which all the most important planets orbit. (Earth has a 23-degree tilt.) Which means that throughout Saturn’s northern summer time, its north pole is tipped towards the solar. From Earth, a lot nearer to the solar than Saturn, we’d be wanting “down” on the rings, seeing them of their full glory.
Saturn’s orbit is nearly 30 years lengthy, so for a lot of the Saturnian yr, we see the rings clearly. On the time of Saturn’s equinoxes, nonetheless, the rings are seen extra almost edge on from Earth, and actually they’re precisely edge on as seen from the solar. However as a result of Saturn’s orbit across the solar is tipped very barely relative to Earth’s, we solely see the rings exactly edge on at Saturn’s equinox when Earth additionally passes by means of the airplane of the rings. This could occur twice close to the equinox as Earth passes “up” by means of the airplane after which “down” once more roughly six months later, successfully erasing Saturn’s rings from our view.
And it simply so occurs that Saturn’s autumnal equinox will happen in Could 2025. And on March 23 our planet will cross by means of the ring airplane, so at the moment, the rings will attain the height of their vanishing act earlier than slowly shifting again into view.
However there’s a caveat: on that date in March, Saturn might be solely 10 levels from the solar within the sky, making it very tough to watch. Unhealthy timing! Whereas Saturn will cross by means of Earth’s orbital airplane once more in mid-November, by that point, Saturn’s axial tilt can have tipped the rings a bit from our vantage level, so we’ll solely see them very almost edge on. The excellent news is that in November Saturn might be simply viewable within the southern sky after sundown, and it’ll nonetheless look almost ringless by means of a telescope. Examine to see if there’s an observatory or astronomical society close to you that’s internet hosting a viewing session!
I’m hoping to take a gander myself; Saturn with out rings might be delightfully odd, and it’s one thing I haven’t seen in additional than seven years. However I’ll additionally sit up for time marching on and the planet brightening as soon as extra as these wonderful rings reveal themselves once more. Someway Saturn with out them simply wouldn’t be Saturn.

