Adolescence is a exceptional interval of improvement and studying, a time when youths discover and adapt to modifications of their social worlds and start to type a way of who they’re and hope to be. It’s a time after they first show a dramatic adaptability to the distinctive cognitive, emotional, bodily, social and sexual calls for positioned on them as they transition from dependence on their mother and father or caregivers to relative independence. It’s also, sadly, a time when the emergence of most psychological well being issues peaks.
The most typical psychological well being considerations going through adolescents at this time are anxiousness issues, and their prevalence has been rising for the previous decade. A survey of tens of hundreds of teenagers confirmed that this prevalence elevated roughly 30 to 40 % between 2012 and 2018, and based mostly on proof from teenagers from Germany, it rose one other 70 % throughout the first few years of the COVID pandemic. But anxiousness issues in younger individuals are largely undertreated.
The one evidence-based behavioral therapies for anxiousness are cognitive-behavioral therapies (CBTs). They contain figuring out triggers of tension after which desensitizing the affected individual to them by means of coping methods similar to optimistic thought reframing or respiration workout routines, together with repeated publicity to the triggers in a protected surroundings. Though CBT is probably the most established therapy for adolescent anxiousness, not all youths who strive it expertise reduction. Amongst those that do, many fail to keep up enhancements over time. A mere 20 to 50 % of sufferers handled for anxiousness with out remedy throughout adolescence stay in remission six years after preliminary CBT. The implications will be long-lasting and extreme. Left untreated, anxiousness can result in extra critical power sicknesses similar to melancholy and substance use dysfunction later in life, higher susceptibility to bodily sicknesses and, in excessive instances, suicide.
On supporting science journalism
In the event you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at this time.
Fortuitously, new discoveries in regards to the adolescent mind are displaying promising paths ahead for the therapy of tension. Present analysis advantages from quickly advancing imaging applied sciences that may reveal patterns of neural exercise and thrilling potential avenues for intervention. These modalities have already supplied entry to the interior workings of the creating mind in laboratory animals and teenagers, and scientists hope they’ll result in new approaches in medical observe that take note of the distinctive modifications within the human mind throughout adolescence. By specializing in the creating mind and the behaviors it generates early on in life, we could also be higher capable of alter anxiety-related recollections, establish cues and conditions that assist to scale back signs, and mitigate the adversarial results of tension for younger individuals earlier than they change into a extra power affliction in maturity.
Prior to now twenty years now we have discovered that the adolescent mind undergoes notable modifications in construction and performance, and these modifications are distinct from these noticed throughout early childhood and maturity. They’re localized, which means sure mind areas change earlier in improvement than others. Areas concerned in feelings, such because the amygdala and the hippocampus, present peak structural and useful modifications throughout the teen years. For instance, throughout adolescence the amygdala’s quantity will increase (a structural change), and so does the best way the amygdala is activated by sure emotional experiences (a useful change). In distinction, mind areas and circuitry related to the regulation of feelings, ideas and actions—the prefrontal cortex, as an illustration—change extra step by step, with improvement persevering with effectively into maturity. These variations in developmental timing could result in an imbalance in communication amongst mind areas, permitting one space to prevail over one other in an adolescent’s decision-making. Accordingly, in emotionally charged or threatening conditions, early-developing emotional areas “win out” over later-developing ones, driving a few of the reactions and responses linked with the behaviors of anxious and unstable teenagers. These regional variations may need served an evolutionary goal. They’ve been linked to heightened sensitivity to emotional and social info which may be important for reproductive success and the survival of the human species. Sadly, these similar imbalances have additionally been related to elevated reactivity to emphasize and higher susceptibility to anxiousness issues.
A core emotion related to anxiousness issues is worry. Though worry is an adaptive response to threats and due to this fact important for survival, persistent worry lengthy after a risk has been eliminated can result in a pathological state of tension. Folks with anxiousness issues have issue figuring out when beforehand threatening conditions have change into protected, they usually could overgeneralize by considering {that a} detrimental expertise in a single state of affairs will recur in different situations.
Many years of animal and human analysis have recognized the fundamental mind circuitry for remembering an acquired worry in adults. The amygdala is vital to creating a worry reminiscence, and elements of the prefrontal cortex are concerned in lowering the energy of worry recollections—a course of often known as extinction. Each the amygdala and the prefrontal cortex are extremely interconnected with a 3rd area, the hippocampus, which performs a task not solely in worry extinction but in addition in figuring out how we expertise worry in numerous conditions. Particularly, the hippocampus offers details about the encompassing surroundings to assist a person resolve whether or not a given state of affairs is extra prone to current a risk (for instance, a bear within the woods) or an absence thereof (a bear on the zoo). A lot of this circuitry is conserved throughout completely different species, enabling the interpretation of primary animal analysis to therapies in people.
Lately researchers have targeted consideration on worry reminiscence and extinction throughout adolescence. These research present that adolescents, like preadolescents and adults, are able to buying a worry reminiscence, however they’re much less capable of extinguish these recollections than individuals in different age teams. After being uncovered to a couple easy pairings of a impartial stimulus (a coloured sq.) with an aversive stimulus (a loud noise), youngsters, adolescents and adults alike present a worry response, measured by sweat gland exercise, to the coloured sq. even when the loud noise not occurs. When preteen youngsters and adults are then offered repeatedly with the coloured sq. with out the loud noise, they start to see the sq. not as one thing predicting the specter of the loud noise however somewhat as a protected refuge from it—the worry reminiscence is extinguished. Adolescents, nevertheless, proceed to react fearfully to the coloured sq..
In instances when worry does get diminished for adolescents, it repeatedly returns with the passage of time. The discovering that adolescents “learn” to extinguish worry much less readily than youthful or older individuals has been replicated in research throughout species (mice, rats and people). Most notably, throughout this developmental interval, the amygdala is far more concerned in sustaining the worry reminiscence than the prefrontal cortex is in initiating the extinction course of. A decrease means to provoke fear-extinction studying is believed to confer a threat for anxiousness. Thus, adolescents could innately be at increased threat.
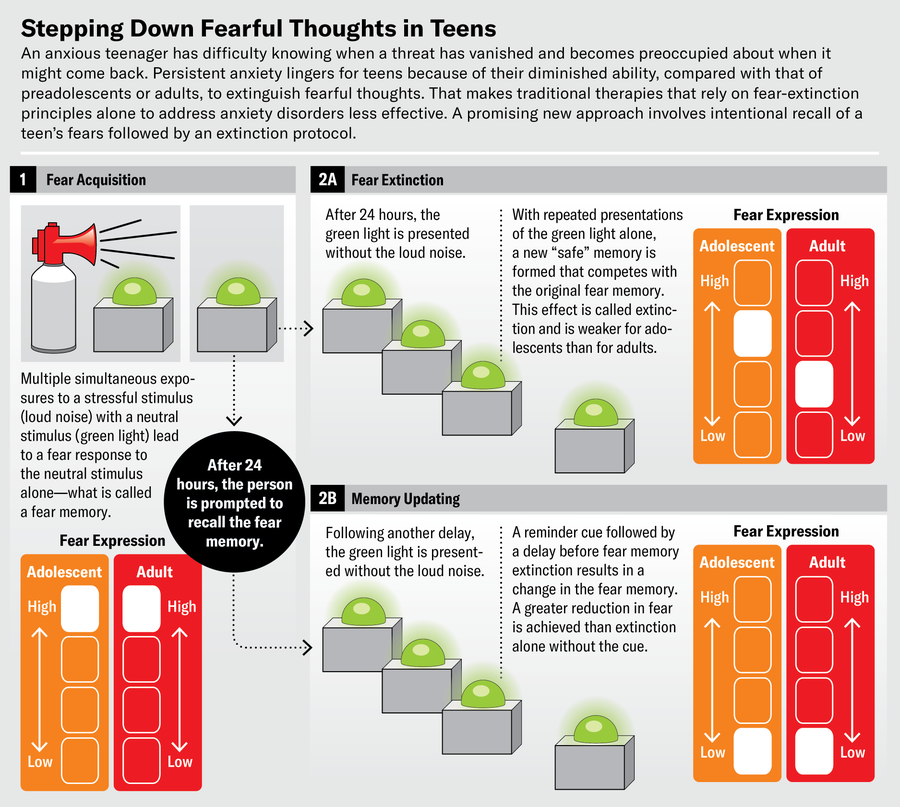
The invention of variations in fear-extinction conduct and mind circuitry throughout adolescence has necessary implications not just for understanding the potential for elevated susceptibility to anxiousness issues but in addition for selecting therapy choices. Behavioral therapies similar to CBT entail figuring out triggers of tension, discovering coping methods and present process a means of desensitization constructed on the rules of worry extinction. However throughout adolescent worry extinction, the involvement of the prefrontal cortex, which is related to the planning and management of conduct, is diminished—which means that for adolescents, the effectiveness of typical exposure-based CBT may additionally be diminished. Collectively, these info increase the query of how we must always tailor therapies for the creating mind. Particularly, how may we use what we all know in regards to the mind’s worry circuitry and the event of worry studying throughout adolescence to information interventions which may be extra profitable in altering teenagers’ worry recollections?
One technique entails conceding the delayed maturation of the prefrontal cortex and circumventing the area in therapy. Quite than counting on prefrontal-based extinction studying, now we have examined an alternate methodology referred to as reminiscence reconsolidation updating. Reminiscence reconsolidation is predicated on the precept that recollections are dynamic, not static. Each time a reminiscence is retrieved, it will get modified. Reactivating a worry reminiscence by presenting a reminder of the worry stimulus opens a time-limited window throughout which the reminiscence itself turns into vulnerable to disruption and alter.
Research in each people and rodents recommend that fear-reminiscence updating is mediated by modifications to the reminiscence within the amygdala. Not like the prefrontal circuitry, which continues to point out developmental modifications into younger maturity, the amygdala undergoes peak maturation throughout midadolescence.
These findings recommend that a method to assist adolescents overcome pathological worry is to introduce what is named a reminder cue to retrieve the reminiscence, adopted by a delay earlier than subsequently extinguishing it. In our lab, we examined this concept in each wholesome adolescents and adults by evaluating their retention of a worry reminiscence after extinction with and with no previous reminder cue. We discovered that though adolescents usually present diminished worry extinction relative to adults, those that had been prompted to retrieve the fearful reminiscence a number of minutes earlier than extinction studying confirmed a dramatic discount in worry the following day in contrast with those that underwent solely extinction studying. In reality, these adolescents’ worry recollections diminished to the identical diploma as noticed in adults.
Historically, extinction studying entails forming a brand new, competing, protected reminiscence that leaves the unique worry reminiscence intact, which means it’s potential for these fearful ideas to return later. The present findings, nevertheless, recommend that with reminiscence reconsolidation updating, the unique worry reminiscence is altered. Thus, the reconsolidation method has the potential to each cut back worry on the time of therapy and reduce the chance that it’ll return.
This analysis is thrilling as a result of it suggests a path to the medical use of reconsolidation updating. Easy modifications to present exposure-based CBT strategies may show efficient in decreasing triggers of worry and anxiousness in adolescent sufferers. This methodology might entail a step so simple as the therapist reminding sufferers why they’re there after they arrive for his or her appointment—the equal of the reminder cue and fear-reminiscence retrieval within the lab setting. Then the therapist might spend a number of minutes establishing a protected rapport with the affected person whereas ready for the reminiscence to enter a labile state throughout the reconsolidation-updating window. Desensitization with publicity remedy might then start throughout the time during which the updating course of takes place. The present variable efficacy of CBT in adolescents with anxiousness issues could also be defined by the truth that some clinicians already use procedures that inadvertently faucet into elements of reconsolidation updating.
Latest makes an attempt to include reconsolidation-updating approaches in treating grownup sufferers with anxiousness and trauma-related issues have yielded some success, however up to now they haven’t been used with adolescent sufferers. The research in adults present short- and long-term discount of signs, particularly for sufferers with particular phobias and post-traumatic stress dysfunction. Though extra primary and medical analysis is required, this methodology appears promising.
Another technique which will assist adolescents extinguish a worry reminiscence entails the usage of security cues that sign there’s nothing to be afraid of. In an experimental setting, a security cue generally is a easy stimulus—an emblem or a sound—that’s distinguishable from and repeatedly contrasted with a worry cue. Outdoors the lab, security cues are available many varieties and are prone to be a stimulus distinctive to the person: a small private object, {a photograph} of a beloved one, a particular scent. We and others have proven that in people and rodents alike, security cues act by recruiting mind areas that present elevated exercise throughout adolescence, together with the amygdala and the hippocampus. The anterior a part of the hippocampus particularly reveals a robust improve in exercise when a security cue is offered alongside a worry cue; the diploma of exercise corresponds to the discount in worry. Moreover, security cues rely much less on the prefrontal cortex than do different types of worry regulation, similar to extinction, highlighting the potential benefit of utilizing a security cue–based mostly method for anxiousness throughout adolescence.
It isn’t possible to keep away from all triggers of extreme worry and anxiousness, so it’s necessary that sufferers don’t change into overly reliant on security cues to the detriment of studying different coping abilities. Security cues could also be a precious instrument for rising the tolerability of the early levels of therapy in order that sufferers don’t drop out. Early therapy classes might embrace steering from the clinician on tips on how to establish and correctly deploy a security cue.
As therapy progresses, cues can provide sufferers a solution to cut back their worry response lengthy sufficient to judge the state of affairs and use instruments from CBT observe. Though analysis on integrating security cues into therapy is in its earliest levels, the tactic reveals nice promise, significantly for adolescents. Our group lately demonstrated in mice that intermittently presenting a security cue throughout an extinction protocol led to raised worry extinction in adolescent mice than noticed in both adolescent (28 to 50 days) or grownup rodents educated with no security cue.
The hope for these rising therapeutic approaches is that we are able to tailor present anxiousness therapies for younger individuals by focusing on the creating mind. It is very important be aware of the truth that the magnitude and depth of the worry response in individuals identified with anxiousness are most likely a lot higher than the worry evoked by aversive stimuli in lab experiments, which are sometimes gentle, narrowly focused and transient. It’s also necessary to do not forget that CBT and antidepressants can deal with anxiousness successfully in many individuals. Sadly, although, for some, these options supply solely restricted or temporary advantages. Due to this fact, the best types of therapy could require a mix of approaches, together with desensitization strategies modified to include reconsolidation updating or security cues, presumably along side antidepressants.
The last word intention is for us to optimize present therapies for teens with anxiousness by focusing on the mind throughout a interval of improvement accompanied by intensive studying and, in so doing, enhance the standard of life for adolescents each within the instant future and later in life.

