A examine printed in Cell Stories Medication reveals that bowel motion frequency considerably influences physiology and long-term well being, with the most effective outcomes linked with passing stools a few times a day.
Earlier analysis has prompt associations between constipation and diarrhea with greater dangers of infections and neurodegenerative circumstances, respectively.
However since these findings have been noticed in sick sufferers, it remained unclear whether or not irregular rest room visits have been the trigger or results of their circumstances.
“I do hope that this work will kind of open clinicians’ minds a bit to the potential risks of not managing bowel movement frequencies,” senior writer Sean Gibbons on the Institute for Techniques Biology instructed AFP, explaining that docs typically view irregular actions as merely a “nuisance.”
Gibbons and his workforce collected scientific, life-style, and organic knowledge – together with blood chemistry, intestine microbiome, genetics and extra – from over 1,400 wholesome grownup volunteers with no indicators of energetic illness.
Contributors’ self-reported bowel motion frequencies have been categorized into 4 teams: constipation (one or two bowel actions per week), low-normal (three to 6 per week), high-normal (one to a few per day), and diarrhea.
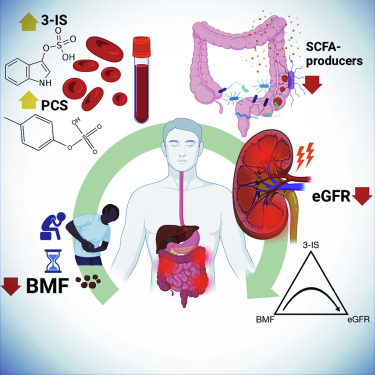
When stools linger too lengthy within the intestine, microbes exhaust the accessible fiber – which they ferment into useful short-chain fatty acids – and as a substitute ferment proteins, producing toxins like p-cresol sulfate and indoxyl sulfate.
“What we found is that even in healthy people who are constipated, there is a rise in these toxins in the bloodstream,” mentioned Gibbons, noting that these toxins are significantly burdensome to the kidneys.
Vegetables and fruit key
In circumstances of diarrhea, the workforce discovered scientific chemistries indicative of irritation and liver harm.
Gibbons defined that in diarrhea, the physique excretes extreme bile acid, which the liver would in any other case recycle to dissolve and take in dietary fat.
Fiber-fermenting intestine micro organism referred to as “strict anaerobes,” related to good well being thrived within the “Goldilocks zone” of 1 or two poops a day.
Nonetheless, Gibbons emphasised that extra analysis is required to outline this optimum vary extra exactly.
Demographically, youthful individuals, ladies, and people with a decrease physique mass index tended to have much less frequent bowel actions.
Hormonal and neurological variations between women and men might clarify the hole, Gibbons mentioned, together with the truth that males typically devour extra meals.
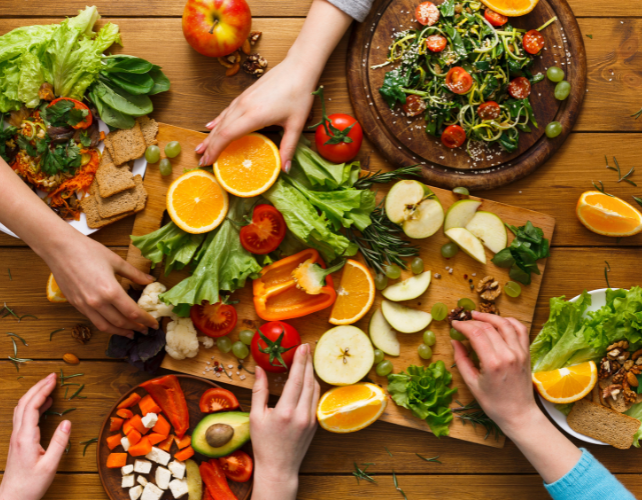

Lastly, by pairing organic knowledge with life-style questionnaires, the workforce painted a transparent image of those that usually fall into the Goldilocks Zone.
“It was eating more fruit and vegetables, that was the biggest signal we saw,” mentioned Gibbons, together with consuming loads of water, common bodily exercise, and consuming a extra plant-dominant weight loss program.
The following step within the analysis might contain designing a scientific trial to handle the bowel actions of a giant group of individuals, adopted over an prolonged interval to evaluate its potential in illness prevention.

