Neutron stars with a penchant for excessive spinning may very well be churning out one of the crucial sought-after particles within the Universe.
These elementary particles are known as axions, and to this point they’re purely hypothetical. If we did handle to search out them, although, we may clear up a number of the largest issues within the cosmos, together with the identification of at the least one form of darkish matter.
So environment friendly ought to these quickly spinning stars be at trapping axions that the elusive particles could also be sequestered in portions excessive sufficient to lastly detect. And that may give us some necessary clues concerning the axion’s nature and properties, comparable to its mass.
Astronomers have been searching for clues about axions since physicists proposed their existence within the Nineteen Seventies. A bit like neutrinos, they’re thought to work together weakly with different matter, making them tough to detect.
In the event that they’re inside a sure mass vary, although, they’re predicted to behave precisely like darkish matter does, contributing to pronounced gravitational results that may’t be accounted for based mostly solely on the quantity of regular matter within the Universe.
Theoretically, axions are anticipated to decay readily into pairs of photons within the presence of a sufficiently robust magnetic discipline, successfully making them seen. Discovering extra gentle with out an easily-determined supply close to a strong magnetic simply could also be an indication of axion decay.
Neutron stars have extremely hefty magnetic fields. These objects are the cores of huge stars which have gone supernova, collapsing into scorching, ultradense lots so squished collectively they behave quite a bit like a single atomic nucleus the scale of a metropolis.
The magnetic discipline spinning out from this object is trillions of instances extra highly effective than Earth’s; robust sufficient to kill you, if different neutron star traits did not get there first.
A pulsar is a sort of neutron star with an added twist: it spins at insanely excessive speeds, typically as quick as millisecond scales. Because it does so, highly effective beams of radio emission blast from the pulsar’s poles, in order that it seems to pulse in house like a cosmic lighthouse. That spin has one other impact: it appears so as to add to the ability of the neutron star’s magnetic discipline.
Physicist Dion Noordhuis of the College of Amsterdam and his colleagues printed a paper final 12 months that discovered these quickly spinning stars are able to producing a 50-digit variety of axions each minute. As they escape from the star, these axions would cross by way of its magnetic discipline and remodel into photons, making the pulsar just a bit bit brighter than it must be.
Analyzing quite a few pulsars, they had been unable to detect any additional gentle. That does not imply these hypothetical particles aren’t there; simply that, if axions are current, there are extra stringent limitations on the sign they could produce.
Axions trapped by the star’s excessive gravity ought to produce a sign too, based on a brand new paper that continues that prior analysis. Over time – maybe million-year timescales – axions ought to accumulate close to the pulsar, lasting the lifetime of the neutron star, producing a faint, hazy layer over the floor of the star.
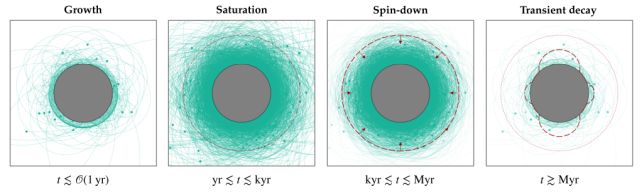
In line with the crew’s evaluation, these axion clouds – in the event that they exist – must be regular for neutron stars, that means they’re current at most, if not all of them. And they need to be extraordinarily dense, round 20 orders of magnitude larger than the native darkish matter density, which implies they need to in flip produce a detectable signature as photons leak free.
We do not know for positive what kind this signature would take, however the crew floated two fundamental prospects. One is a steady sign, a slender line within the radio spectrum of the pulsar at a frequency akin to the axion’s mass. We do not know what this mass is, however the line’s absence within the spectrum may slender it down.
The opposite is a burst of sunshine on the finish of the neutron star’s lifespan, the purpose at which it stops emitting radiation. This course of is projected to naturally take trillions of years; the Universe is not sufficiently old for it to have occurred but, so we’re unlikely to watch any axion-bursts from dying neutron stars quickly. That makes the continual sign one of the best wager.
As with the surplus gentle, the researchers had been unable to search out proof of a neutron star axion cloud round close by pulsars. However the non-detection allowed for the strongest constraints but on the mass of the axion inside a sure vary, with out counting on the belief that axions are darkish matter.
The analysis additionally paves the best way for future searches, giving us new methods to search for, and perceive the properties of, this mysterious, elusive particle.
The analysis has been printed in Bodily Overview X.

