When the Apollo 17 astronauts returned from the moon in 1972, they couldn’t have identified that they’d be the final people to journey deep into outer area for greater than 50 years. However no astronauts have ventured beyond Earth orbit since, at the same time as Presidents George W. Bush, Barack Obama, Donald Trump and Joe Biden have all deliberate lunar missions. Lastly, NASA is getting ready to ship individuals again to the moon on the Artemis II flight, scheduled to elevate off within the fall of 2025. Why has it been so tough?
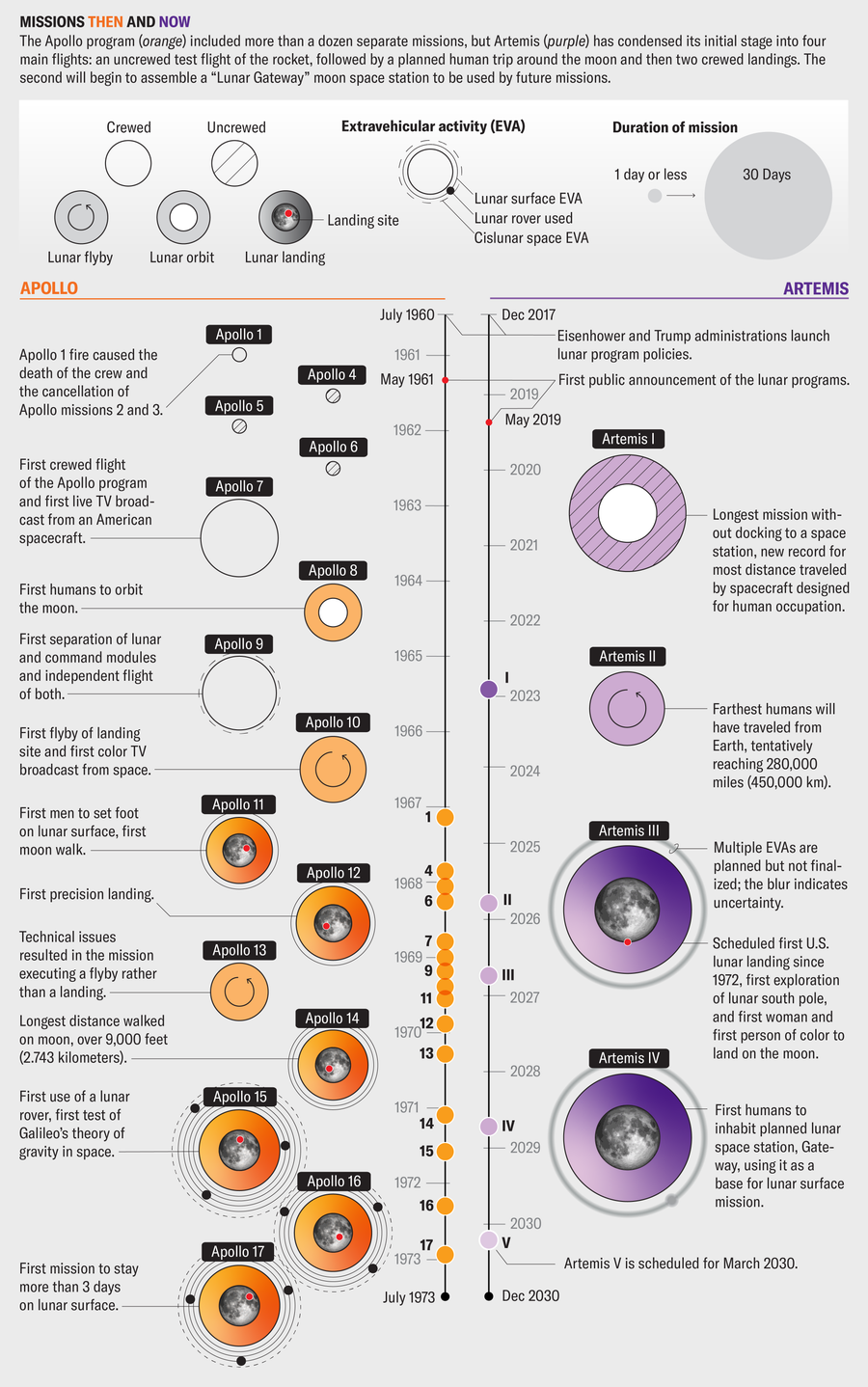
This new mission is just like the Apollo 8 flight of 1968, when three individuals circled the moon with out touchdown after which traveled again to Earth. Artemis II will ship 4 astronauts on a 10-day journey across the moon on the primary crewed check of NASA’s new Area Launch System (SLS) rocket and Orion area capsule. Though the U.S. has had many years to get higher at such journeys, the upcoming journey resembles its mid-century cousin in that it will likely be removed from straightforward.
Selecting to do issues “not because they are easy but because they are hard” is a part of the rationale President John F. Kennedy gave in a well-known 1962 speech attempting to impress help for the Apollo program. And what was true then stays so at present—in actual fact, reaching the moon could also be much more tough than it was many years in the past.
On supporting science journalism
When you’re having fun with this text, take into account supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you might be serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world at present.
NASA’s Artemis program has been stricken by lengthy delays, value overruns and shock issues. It has these in widespread with many terrestrial applications, comparable to subway upgrades and freeway development, which additionally appear to take for much longer, and sometimes value far more, than they did within the (dubiously) good previous days. Is it actually tougher to construct nice issues now? And with regards to the moon, why ought to replicating a feat the U.S. completed greater than half a century in the past take so lengthy?
Artemis’s subsequent step is actually an Apollo 8 redo, however this system has grand ambitions that attain past the moon. “In the end, our stated goal is Mars,” says Matthew Ramsey, Artemis II’s mission supervisor. “That’s very difficult—getting to Mars and living on Mars—and so we take it in bite-sized chunks.”
This system’s first mission, Artemis I, despatched an uncrewed spacecraft across the moon and again in 2022. After Artemis II, the third via sixth installments will put individuals on our pure satellite tv for pc after which arrange items of the Lunar Gateway, an area station orbiting the moon. Later missions may even concentrate on organising liveable camps on the lunar floor.
The Orion capsule for the upcoming Artemis II mission undergoes testing at Kennedy Area Middle in Florida.
The Artemis program, barely off the bottom, has already seen lengthy delays, and this system faces important issues, specified by a latest audit from NASA’s workplace of the inspector normal. First, it can have devoured $93 billion by 2025, billions greater than anticipated. Second, the Artemis I journey revealed “critical issues that need to be addressed before placing crew on the Artemis II mission,” in keeping with the audit. The Orion capsule’s warmth defend, as an example, broke down in a different way than engineers had predicted, for causes they don’t but perceive. Bolts on the spacecraft confronted “unexpected melting and erosion.” And the facility system skilled anomalies that would go away the long run crew with out ample power and redundancies and perhaps with out propulsion or pressurization.
These “anomalies”—the time period area sorts use for large issues—“pose significant risks to the safety of the crew,” in keeping with the report. And so they got here on high of different {hardware}, information and communications challenges. Moreover, the inspector normal discovered that the preliminary launch brought about unexpected harm to the system, leading to repairs to the tune of greater than $26 million, a a lot heftier invoice than the crew had budgeted for. That’s loads of hitches and some huge cash—particularly for a mission that received’t accomplish many firsts we didn’t obtain again within the Sixties.
It could seem unusual that at present’s lunar missions are so difficult on condition that we’ve finished this earlier than. However the circumstances aren’t the identical, says Scott Tempo, director of the Area Coverage Institute at George Washington College. “The world environment is very different,” he says. The U.S. is not in an area race—an existential battle to remain forward of the communists and be the primary to do issues past Earth. Again then, chilly struggle dynamics had been at play, and newly unbiased international locations had been deciding which governing system to observe—a call which may (theoretically) be influenced by a democratic nation’s means to discover area. Such “soft power,” the pondering went, might present that the American manner was one of the best ways whereas utilizing the nation’s missilelike rockets to indicate onerous army dominance. Given these stakes, the U.S. authorities was prepared to throw big quantities of cash on the Apollo program in a short while.
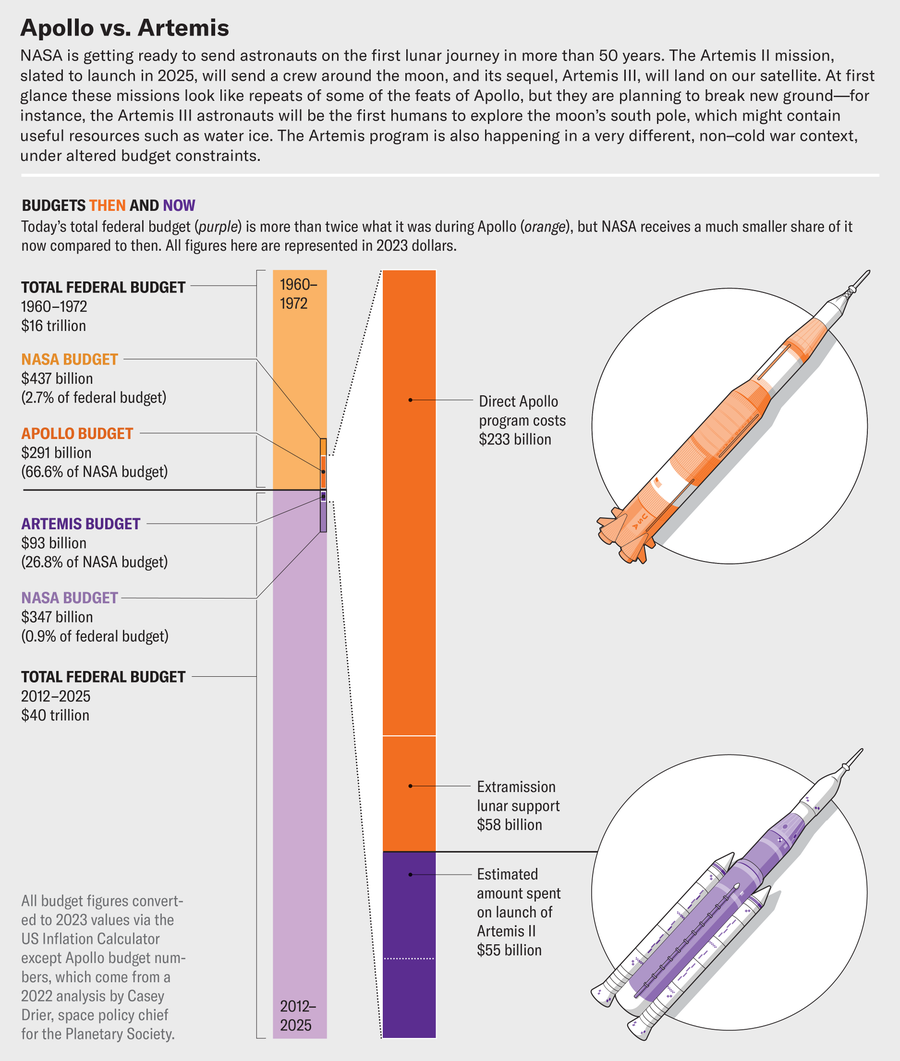
Artemis is pricey, however Apollo was exorbitant: this system value round $290 billion in at present’s {dollars}, in keeping with the Planetary Society, in contrast with Artemis’s $93 billion. In these years NASA was typically blessed with 4 % of the nation’s finances. At the moment it’s fortunate to get round 1 %, with the extra burden of many different spacecraft, telescopes and analysis tasks past human spaceflight to fund.
That budgetary lower is smart, in keeping with John Logsdon, professor emeritus at George Washington College and founding father of the Area Coverage Institute. “There’s no reason to spend money like it was a war,” he says. “There’s really no national interest or political interest that provides the foundation for that kind of mobilization at this point.”
Zane Wolf (information visualization), Brown Chicken Design (spacecraft illustrations)
These looser dynamics shrink the wad of money out there and set the planning of area missions on a extra meandering path. Within the Sixties Kennedy declared the nation would go to the moon in that decade, and it did. In fashionable occasions spaceflight plans established by one president are sometimes canceled by one other, solely to be resurrected later in a special type. Consequently, the trajectory towards the moon (and past) zigs and zags.
The world order has additionally modified, and area missions are usually world cooperations now, Tempo notes. The Artemis program is a collaboration involving Japan, Canada, the United Arab Emirates and the European Area Company. That worldwide participation is in actual fact an enormous a part of this system’s level. “Artemis has scientific purposes—going back to the moon and all that,” Tempo says. “But it also is a way of shaping the international environment for space.” That molding is far more important than it was within the Sixties, when people relied much less on above-Earth infrastructure. At the moment orbiting spacecraft allow every part from GPS capabilities to missile warning to banking. Convincing different international locations to see and deal with area as a worthwhile useful resource, by working with them and establishing behavioral norms, helps us maintain area protected and the gamers up there accountable. “Rules are made by people who show up,” Tempo says.
That’s a extra nebulous aim than successful a race. “If there were nice, sharply defined motivations, things would be a lot simpler,” Logsdon says. However working with different international locations, a number of of whom are constructing {hardware} for Artemis, takes longer than going it alone—simply as doing a gaggle undertaking can grate greater than merely pulling a solo all-nighter. In keeping with the NASA inspector normal, the worldwide nature of this system can be rising the prices, and NASA doesn’t have an overarching technique for coping with all of the companions it’s introduced onboard.
In Tempo’s view, nevertheless, none of these components is the primary stumbling block on the lunar trajectory. The most important problem, regardless that the U.S. has already been to the moon, is that we haven’t been to the moon lately. “We stopped, and then we forgot,” he says. Simply betrigger you ran the Olympic marathon 50 years in the past, he continues, doesn’t imply you can do it once more tomorrow.
In the case of Artemis, the marathon additionally entails new, extra sophisticated know-how. The fundamentals of the rocket facet of the equation haven’t modified that a lot: large rockets are basically bombs that increase issues to area. And lots of the gamers are the identical. Boeing labored on the Saturn V rocket that despatched Apollo missions upward. For Artemis, the corporate designed and constructed the SLS core stage, a large piece of equipment that stands 212 ft tall and is sort of 28 ft throughout. This part supplies gas to the engines that heave SLS from the bottom and sends it flying the fitting manner—courtesy of the Boeing-created avionics system that’s additionally onboard. The corporate, at the moment beset by controversy over quality-control points in its planes in addition to a malfunctioning spacecraft that stranded two astronauts on the Worldwide Area Station, can be answerable for rocket phases for later Artemis missions.
There are some large variations between Boeing’s vintage work on Saturn V and its fashionable cousin. This time they constructed the rocket phases utilizing computer-controlled machining, in addition to a friction-based welding method that doesn’t soften and warp metallic. The corporate additionally makes use of computer systems to research the rocket phases’ states of being and monitor how they’re behaving in actual time—a perspective Apollo lacked.
Northrop Grumman, in the meantime, handles the rocket boosters, that are strapped onto the edges of the core stage. These give SLS greater than 75 % of its oomph at launch. A lot of the boosters’ engineering hails from the area shuttle program, and in some circumstances elements of their {hardware} truly flew on shuttle missions. These boosters, like missiles, use stable rocket gas moderately than liquid. “You want to get away from Earth’s gravity well and out of the thick part of the atmosphere where drag is high as fast as you can,” says Mark Tobias, SLS booster deputy engineer. “And that’s what solid propulsion really does. It’s raw horsepower.”
However the plan to make use of {hardware} from earlier area applications is a bit cobbled collectively. The Area Launch System, as an example, was initially designed for the Constellation program, a technique arrange beneath the George W. Bush administration to complete constructing the Worldwide Area Station and to reestablish a human presence on the moon. Congress mandated that the rocket reuse know-how from the then defunct area shuttle program. However Obama canceled Constellation in 2010, and in 2017 Trump anointed the Artemis program, with the aim of lastly sending individuals again to the moon and paving the way in which for exploring Mars. Once more, the brand new plan required that NASA use a number of the know-how that had been developed for Constellation, which in flip entailed repurposing previous area shuttle know-how. These mandates had been pushed by congresspeople representing areas that housed manufacturing facilities for shuttle elements. However the carryover and conversion of these applied sciences have proved tough. In keeping with a report from the NASA inspector normal, bringing the rocket elements into the fashionable period—as an example, changing asbestos elements—and retrofitting them for a brand new rocket system has value far more than anticipated.
Aerospace firm Aerojet Rocketdyne builds the engines, and as with the rocket boosters, making previous shuttle engines work for Artemis has been onerous and costly. SLS is a a lot taller rocket than the area shuttle. The stretched dimensions required altering the engines to take care of oxygen flowing in at increased pressures. The engines are additionally nearer to the boosters than they had been on the shuttle. “It’s an extreme heating environment,” says Mike Lauer, director of the engine program, so it requires excessive insulation.
The Artemis engines may even expertise a extra irradiated surroundings going to the moon (and later to Mars) than they did in orbit on the shuttle. Coping with that change concerned tinkering with the pc that lives on every engine, which Lauer calls its “brain.” These brains additionally wanted a modernization, as computer systems are a lot completely different than within the Nineties (you might need observed). The brand new and improved brains can monitor the engines—together with throughout an impending catastrophe. “Things can be done to correct or save the mission and, in a worst-case scenario, shut an engine down before it blows up,” Lauer says. Throughout Apollo, engineers couldn’t have identified about issues quick sufficient to resolve them. At the moment, he says, regardless that astronauts are principally using a bomb, “that bomb is being watched very closely.”
“Artemis has scientific purposes. But it also is a way of shaping the international environment for space.”
—Scott Tempo George Washington College
The retrofit was difficult, although, and required discovering new suppliers as a result of many who had labored on the area shuttle didn’t make the related elements anymore. In the end the purpose is that this: generally it’s simpler to design and construct the home you need than to renovate a fixer-upper with a toilet subsequent to the kitchen and cabinets at awkward heights.
Speaking of using bombs, NASA treats people with a softer contact than it did within the Sixties, when it was swooping up fighter pilots and capturing them into area. That’s obvious within the design of Orion, constructed by Lockheed Martin.
Blaine Brown, director of Orion’s mechanical methods, and his crew ran calculations about what sorts of rigors these methods would maintain up towards and designed them to resist multiples of what anybody expects them to expertise, whether or not excessive temperatures or intense acceleration forces. As they refine the spacecraft, engineers proceed to run detailed simulations on Orion’s supplies and the stresses the capsule shall be beneath, getting down into the small print of potential weaknesses in a grainy manner that the slide guidelines of the Sixties couldn’t deal with. Additionally they do x-ray inspections of the welds and the blocks that type the warmth defend, which retains the capsule from burning up because it streaks again via the environment. The crew will get extra information than prior to now on how the area car does in flight—simply because the rocket contractors do—in addition to a greater means to speak.
“We understand way more” than engineers throughout Apollo did, Brown says. Nonetheless, the sudden pops up, as with Orion’s degraded warmth defend, which, regardless of all the flowery pc simulations, was lacking chunks after its first reentry. Even with at present’s computational energy, there’s no assure of good outcomes. Apollo clearly labored with out that evaluation. However as soon as such predictive capabilities can be found, engineers are virtually beneath an moral obligation to make use of them to grasp exactly what they’ll be subjecting the astronauts to.
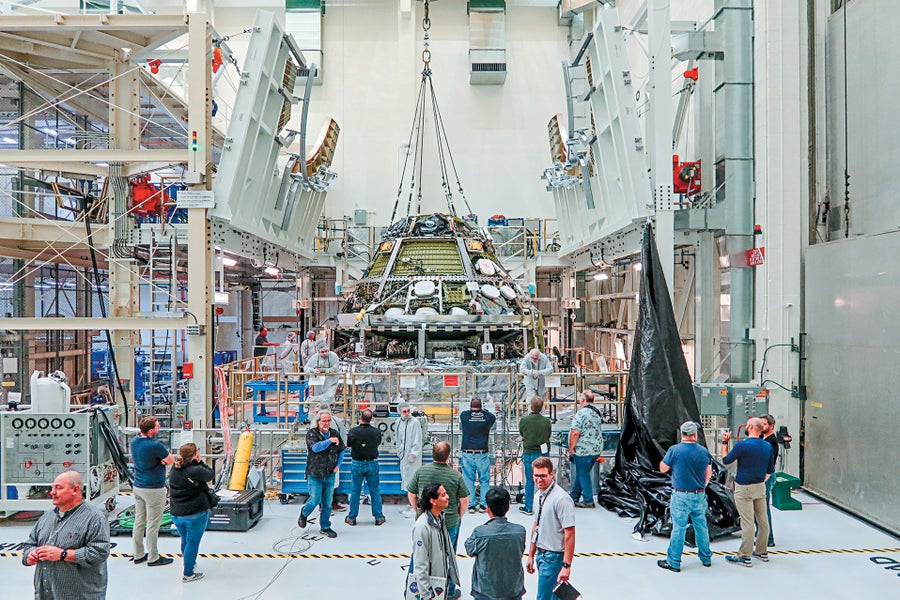

Engineers join two elements of the Orion spacecraft, the crew and repair modules, at Kennedy Area Middle.
Society’s angle towards threat has modified for the reason that area race, says bioethicist Jeffrey Kahn of Johns Hopkins College. He’s sat on panels tasked with independently analyzing the ethics of astronaut life for the Nationwide Academy of Sciences—together with which risks are well worth the journey in any respect. That cost-benefit equation churned out completely different calculations within the Sixties. The potential large reward of successful the area race towards the communists was usually held to be price extra hazard. At the moment the motivations for the mission are murkier, the stakes are decrease, and the resultant rewards don’t justify as a lot threat.
Again then, the powers that be had been additionally unaware of a number of the dangers we now know exist, area being a brand new frontier on the time. Astronauts hailed from that “right stuff” mildew of previous. “Astronauts rode motorcycles and drove fast cars,” Kahn says, along with being check pilots. At the moment a greater variety of individuals go into area for a bigger variety of causes. “Astronauts are not some separate species,” Tempo says. Maybe, then, we worth their lives extra like we worth our personal.
If one thing did go unsuitable, the response to that hypothetical accident would most likely be extra vehement than it was when, for instance, three astronauts died within the 1967 Apollo I hearth. After that tragedy there was minimal name for cancellation and even important delay. Now, Logsdon says, the Artemis program won’t have sufficient political help to outlive a fatality. So Artemis II and the missions to observe all should be as protected as they are often to proceed to be in any respect.
Getting again to the moon isn’t the one fashionable problem beset by delays and finances blowups. Many large-scale endeavors have grown tougher and costlier over time. The New York Metropolis subway system, as an example, was initially in-built simply over 4 years and had 28 stops; a brand new subway line within the metropolis with simply three stops, completed in 2017, took 17 years. Scientists developed nuclear weapons from scratch in three years within the Forties at a value of about $35 billion in at present’s cash; the present nuclear weapons modernization program will take not less than 30 years and value greater than $1.5 trillion. On the finish of World Conflict II the U.S. was whipping up an plane provider a month; the newest one took greater than a decade.
Freeway delays and large spending are the specialty of Leah Brooks, a professor at George Washington College’s Trachtenberg Faculty of Public Coverage and Public Administration. Her analysis has discovered that asking residents for enter on tasks—a requirement of many giant governmental enterprises nowadays—is one important reason for street woes. This enter is usually a part of an environmental evaluation that’s required earlier than a undertaking begins. Bearing in mind the “citizen voice,” as Brooks calls it, may end up in costlier routes which have fewer destructive environmental impacts or are much less disruptive to residents’ lives but in addition may require extra mitigating infrastructure, comparable to sound obstacles. Previously, authorities didn’t should ask for everybody’s opinion (or care a lot concerning the surroundings). Take the Tennessee Valley Authority, Brooks says, an entity established within the Thirties to assemble dams to scale back flooding and generate electrical energy. “They don’t consult anybody,” she says. “They just build it.” Kennedy didn’t select to go to the moon as a result of he had requested what everyone thought, both.
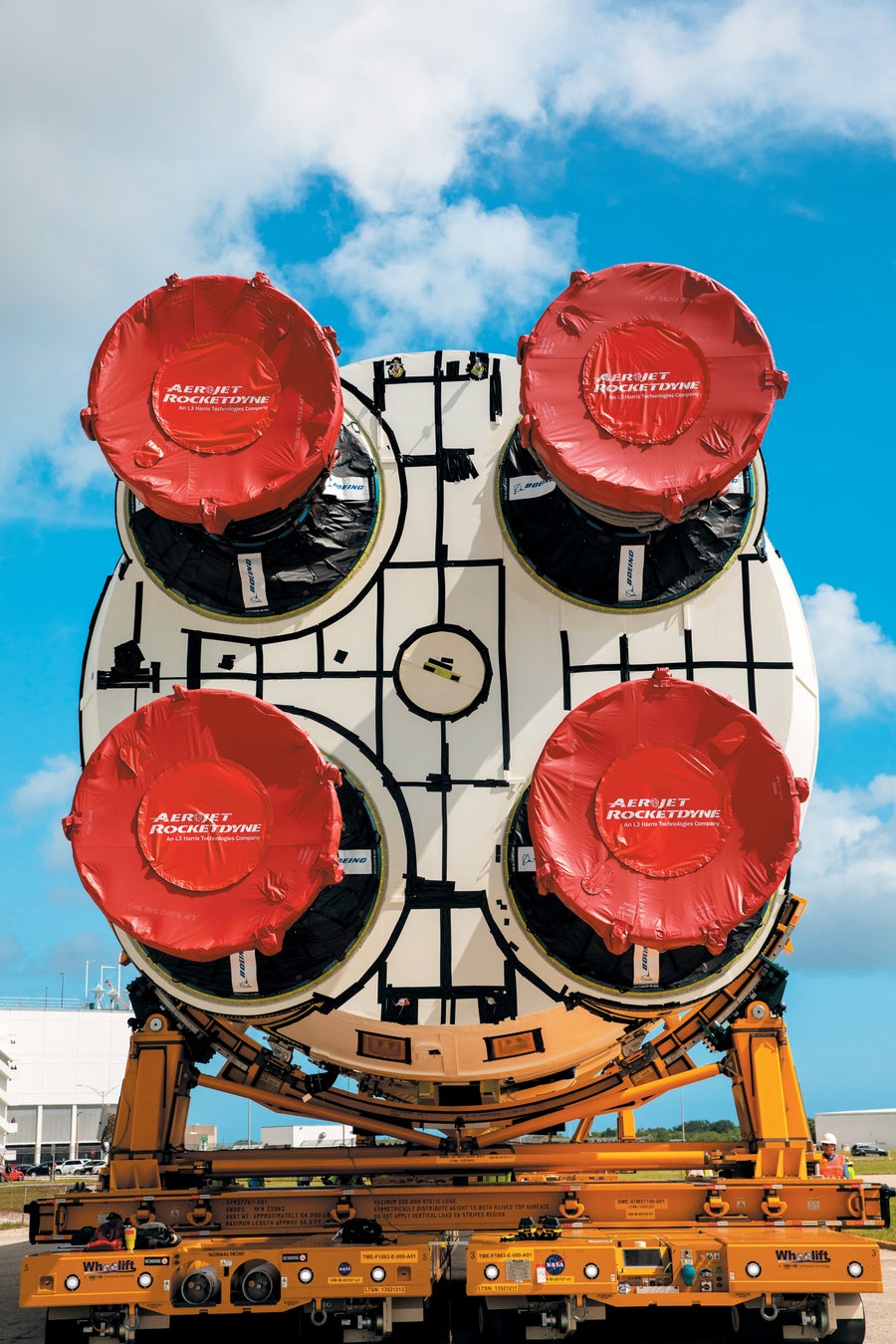

The core stage of the Area Launch System rocket traveled from NASA’s New Orleans meeting facility to Kennedy Area Middle in July 2024. Will probably be readied there for the Artemis II mission.
Brooks’s findings might apply to any endeavor that entails an environmental influence assertion—a doc that lays out the results for the pure surroundings and requires an open interval of public remark. One such doc exists for the earlier Constellation program; it was re-upped for NASA’s “post-shuttle human spaceflight program.”
In Brooks’s view, although, the largest distinction between previous and current could also be that we construct issues higher now, which is pricey and takes longer. That is probably not true of, say, house home equipment, however it’s true of these freeway sound obstacles and, maybe, of spaceships. For Artemis, having a extra sturdy rocket system, asking individuals what they assume, retaining individuals safer and dealing with world companions are most likely higher for this world—even when they don’t end in expedience off-world. That lack of expedience might even be factor. At the moment, Logsdon says, you don’t hear many individuals arguing towards the Artemis program. In distinction, Apollo wasn’t truly common with the general public. In 1961 extra individuals opposed government-funded human journeys to the moon than had been in favor. In 1965 a majority opposed such journeys, and in 1967 the hole between “in favor” and “opposed” had grown to almost 20 proportion factors, in keeping with analysis from area historian Roger Launius.
The brand new manner of going deep into area in the end ends in a safer, better-understood system which may meet with extra public approval—at house and overseas. And in addition to, it’s at all times been true that we select to do it as a result of it’s onerous—so what if it’s tougher? And what’s the frenzy? It’s not a race.

